 EUROPEAN COMMISSION
EUROPEAN COMMISSION
Brussels, 17.11.2015
SWD(2015) 207 final
COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT
Accompanying the document
Report from the Commission to the European Parliament and the Council on the application of the Postal Services Directive (Directive 97/67/EC as amended by Directive 2002/39/EC and Directive 2008/6/EC)
{COM(2015) 568 final}
Contents
1.Introduction and background
1.1.Postal Services in the Digital Age
1.2.The Postal Services Directive
1.3.Purpose and Scope of the Fifth Application Report and Staff Working Document
2.Application of the Postal Services Directive 2008/6/EC
2.1.Transposition and Application of Directive 2008/6/EC
2.2.Regulation of Postal Services
2.2.1.National Regulatory Authorities
2.2.2.Authorisation and Licensing Regimes
2.3.The Universal Service: Basic Postal Services for All
2.3.1.Designation of Universal Service Provider(s)
2.3.2.Services Provided under the Universal Service Obligation
2.3.3.Frequency of the Universal Service
2.3.4.Studies on User Needs and the Universal Service Obligation
2.3.5.Tariffs for Universal Service Products
2.3.6.Price Regulation
2.4.Financing the Universal Service Obligation
2.4.1.Regulatory Accounting
2.4.2.Net Cost of the Universal Service Obligation
2.5.Access to Postal Services, Network and Infrastructure
2.5.1.Access Points
2.5.2.Access to Postal Infrastructure
2.5.3.Access to the Postal Network
2.6.Quality of Service
2.7.Protection of Users
2.8.Internal Market for Postal Services: the Cross-Border Dimension
2.8.1.Legal Obligations and Regulatory Oversight
2.8.2.Tariff Principles
2.8.3.Customs and Security Controls
2.9.Data Collection
2.10.Value Added Tax (VAT)
2.11.Application of Competition Rules
3.Market Developments in the Postal Sector
3.1.Sector Overview
3.1.1.Ownership Structures of Universal Service Providers
3.1.2.Financial Position of Postal Operators
3.2.Letter Post Markets
3.2.1.Letter Volumes and Revenues
3.2.2.Competition in Letter Post Markets
3.2.3.Cross-border Letter Post
3.2.4.Outlook
3.3.Parcel and Express Markets
3.3.1.Parcel and Express Markets Overview
3.3.2.Parcel Volumes and Revenues
3.3.3.Competition in Parcel Markets
3.3.4.Cross-border Parcel Delivery
3.4.Employment in the Postal Sector
3.4.1.Overview
3.4.2.Employment in Universal Service Providers
3.4.3.Type of Employment and Working Conditions
3.4.4.Social Partners and Industrial Relations
3.4.5.Managing Restructuring
4.Conclusion
5.Annex on the Calculation of the Net Cost of the Postal Universal Service Obligation
1.Introduction and background
1.1.Postal Services in the Digital Age
Postal services have a central role in creating and sustaining an effective and dynamic single market and are vital for the wider economy. In 2013, the most recent year for which statistics are available, the universal service area alone (i.e. products and services falling within the scope of the universal service) accounted for more than EUR 23 billion for the EU28. Over 85 billion letter post items were dispatched by universal service providers in the EU, as were nearly 2 billion parcels. The postal services sector is also an important employer with about 1.2 million people employed by universal postal service providers (USPs) in 2013, plus those working for other letter and parcel delivery operators. The European Express Industry was estimated to employ 272,000 in 2010, predicted to grow to 300,000 by 2020.
The role of postal services is however changing rapidly and fundamentally, even more so since 2008. On one hand paper-based communications have declined in many Member States, while electronic-based communication witnessed significant growth. On the other hand, new technologies make shopping online more convenient and therefore increase the number of packages and parcels conveyed by postal operators. Consequently parcel and express revenues now account for more than half of the postal sector's total revenues, compared to 2007 when letter post was responsible for over half.
With full market opening in the postal sector accomplished in all Member States, the universal service providers now face the possibility of competition from new market entrants in the letter segment, though in reality the level of competition differs significantly between Member States and is relatively low in majority of them. In the parcel segment, competition appears to be intensifying to take advantage of the opportunities offered by e-commerce.
In response, universal service providers have increased their efficiency and restructured their operations to reduce costs. Many postal operators and other delivery companies are now more innovative and have developed new services, such as apps to track parcel delivery and electronic document exchange solutions. As a result however, postal workers' jobs and the skills needed for them have changed and overall employment (and in particular employment at universal service providers) has decreased.
Nevertheless, a high quality universal service at affordable prices is provided in all Member States. Further improvements have been made in the quality of service, innovation and customer orientation, business efficiency, the work of national regulatory authorities and collaboration with social partners. Shifts in the communications landscape and the advent of the Digital Single Market do however mean that the needs of postal users will continue to evolve and both legislation and regulatory oversight will need to keep pace with these developments, particularly to ensure the ongoing protection of all users and the sustainability of the postal sector.
1.2.The Postal Services Directive
The overall objective of European postal policy is to ensure that efficient, reliable and high-quality postal services are available on at least five working days per week throughout the EU to all its citizens and businesses at affordable prices. In line with the principles of subsidiarity and the differences in the postal markets of Member States, the Postal Services Directive is a framework directive which gives a considerable degree of flexibility to the Member States, allowing them to adapt elements of domestic postal services to their own particular needs.
The First Postal Services Directive, Directive 97/67, was adopted in 1997 after a lengthy period of analysis and consultation. It followed the broad aims set out in the Green Paper on the development of the single market for postal services published in June 1992, which inter alia stated that the analysis showed a sector with underlying structural problems, wide divergences between Member States and the absence of a clear Community-wide approach. Consequently the First Postal Services Directive aimed to improve domestic and intra-EU postal services by addressing the low quality of service and efficiency; the lack of customer focus, choice and innovation; limited cooperation between operators; and ongoing state subsidies.
Among the key elements of the First Postal Services Directive were the establishment of a universal service, with minimum scope, frequency and quality of service requirements, a number of tariff principles and the creation of independent national regulatory authorities (NRAs) for postal services. An essential element of the modernisation strategy was the ‘gradual and controlled liberalisation of the market’. In 2002, as a further step in that direction, the Second Postal Services Directive, among other amendments, reduced the price and weight limits for the reserved area, thus reducing the scope of the monopoly of the national postal operators.
In February 2008 the Council and the European Parliament adopted the Third Postal Services Directive which introduced the legal basis for the accomplishment of the internal market for postal services by providing for a last legislative step in the process of gradual market opening. It set an agreed deadline for full market opening of 31 December 2010 for 16 Member States and 31 December 2012 for the (then) remaining 11 Member States. References to the Postal Services Directive (PSD) or 'the Directive' refer to the consolidated Postal Services Directive (unless otherwise stated).
In addition to setting a timetable for full market opening, the Third Postal Services Directive modified other provisions of the Directive to render them more compatible with ‘full market opening’. Revisions and additions included strengthening the tasks and competences of NRAs; changes in the manner in which universal service could be provided and financed; requiring certain elements of the postal infrastructure (such as address databases and letter boxes) to be accessible to multiple operators; strengthening and broadening the legal requirements for information and data collection by NRAs; and extending consumer protection provisions. The Directive also contains a specific provision requiring the Commission to provide assistance to Member States on its implementation, including on the calculation of any net cost of the universal service, which was initially set out in Annex (I) entitled "Guidance on calculating the net cost, if any, of universal service" and is further addressed as an Annex to this Staff Working Document.
1.3.Purpose and Scope of the Fifth Application Report and Staff Working Document
This Staff Working Document accompanies the Application Report and provides more detailed information on how the Directive has been implemented, market developments and calculations of the net cost of the Universal Service Obligation that have been found to be consistent with the Directive.
The Application Report and Staff Working Document cover developments from late 2008 (when the Fourth Application Report was published) to 2015, although official postal statistics are only available up to 2013 due to the time lag in gathering data and some other estimates, in particular those for the parcel sectors, are for earlier years. Sources used for this Report include studies commissioned by the Commission on Main Developments in the Postal Sector (2008-2010), Pricing behaviour of postal operators and Main Developments in the Postal Sector (2010-2013), a number of reports by the European Regulators Group for Postal Services (ERGP), contributions in the context of the Postal Directive Committee (PDC) and the Postal User Forum, documents and contributions linked to the 2012 Green Paper, An integrated parcel delivery market for the growth of e-commerce in the EU, and the 2013 Communication, A roadmap for completing the single market for parcel delivery Build trust in delivery services and encourage online sales. Eurostat data up to 2011 and the Commission's own statistics, for period after 2012 when Eurostat decided to stop dedicated collection of statistical data for the postal sector, have also been used. The latter are referred to in the Report and Staff Working Document as 'European Commission Postal Statistics. Universal Postal Union statistics have also been used.
The period late 2008 to 2015 is of particular significance for the postal sector in the EU for two main reasons. First, the Application Report and Staff Working Document cover the period in the run up to and directly after full market opening in all EU Member States. Second, there are profound changes in the communications and postal sector, compounded by the economic situation following the 2007/08 financial crisis, which are fundamentally impacting the postal market. Letter volumes have fallen substantially since 2008 in most Member States and by around 40% in the one most affected (Denmark). Parcel deliveries are increasing, but require a different postal infrastructure as well as different skills and patterns of employment for employees.
2.Application of the Postal Services Directive 2008/6/EC
2.1.Transposition and Application of Directive 2008/6/EC
All EU Member States have now transposed Directive 2008/6/EC. This Staff Working Document covers the EU Member States only, unless stated otherwise.
The three European Free Trade Area (EFTA) Members of the European Economic Area (EEA), Iceland (IS), Lichtenstein (LI) and Norway (NO), are not covered by this Staff Working Document as they have not yet transposed Directive 2008/6/EC. It should, however, be noted that the Norwegian government submitted the bill for a new Postal Service Act to the national parliament (i.e. Storing) on 24 April 2015; this bill is implementing Directive 2008/6/EC and also contains certain changes to the universal service.
The Commission continues to monitor whether the legislative measures adopted by Member States constitute a complete transposition of the Directive and if the different elements of the Directive are implemented correctly. Since 2008 the Commission has initiated infringement proceedings against two Member States, namely Belgium and Croatia, on issues of content (rather than timing) in the postal acquis.
2.2. Regulation of Postal Services
2.2.1.National Regulatory Authorities
Independent national regulatory authorities (NRAs) play a key role as they are the competent bodies who – after an appropriate implementation into national legislation
– oversee the Directive's application. NRAs are defined as "the body or bodies, in each Member State, to which the Member State entrusts, inter alia, the regulatory functions falling within the scope of this Directive" (Article 2 (18)). They “have as a particular task ensuring compliance with the obligations arising from this Directive (…)” and “may also be charged with competition rules in the postal sector” (Article 22).
All EU Member States have established an independent NRA for the postal sector. Most Member States combine the regulation of the post and electronic communications sectors, in some cases alongside other network industries (e.g. rail transport and energy). The model of a multi-sector regulator has gained further momentum in the reporting period and regulators who cover the postal sector alone are the now the exception.
Regulatory independence can be reinforced through qualifications, fixed terms of office and legal protection against dismissal without cause. Senior NRA officials should not be permitted to work for the public postal operator or other interested parties immediately after serving with the NRA in order to prevent any actual or perceived conflict of interest. In general the organisational set-up of most NRAs is likely to foster regulatory independence, though there is still room for improvement to bring some governance procedures in line with best practices, for example where the minister responsible for postal policy is able to appoint or dismiss the head of the NRA and approves the NRA's budget.
To help ensure effective regulatory oversight, the PSD requires that NRAs are provided with all necessary resources in terms of staffing, expertise and financial means for the performance of their tasks. Overall, available figures suggest that combined resources for postal NRAs have changed little or decreased slightly since 2008, with an estimated 344 people employed and a budget of EUR 35 million in 2012 for the EEA. The financial and personnel resources available to NRAs vary substantially between Member States. Larger Member States with bigger postal sectors have larger NRAs, although the increase in resources is not proportional to market size. The postal sector’s role in facilitating e-commerce, the growth of the parcel segment and rapid changes in technology means that NRAs should be ready and equipped to face new challenges as they arise.
To ensure compliance with the obligations arising from the Directive, NRAs require sufficient enforcement powers. In some Member States enforcement powers are comprehensive, for example where the NRA can levy significant fines, issue remedial orders or seek court enforcement, though in some instance these powers are more limited.
The vast majority of NRAs appear to have satisfactory procedures in terms of transparency, fairness and clarity. Examples of such procedures include the publication of key documents in national languages, opportunities for the public to comment on proposals and public reporting. At least fifteen NRAs (EU and EEA) show a high level of transparency.
Member States must also, if appropriate, provide for coordination between the NRAs, National Competition Authorities (NCAs) and the consumer protection authorities (Article 22(1)). From a procedural point of view, Member States may entrust enforcement of the competition rules to the NRA, the NCA, or both. Competition rules tend to be delegated to the NCA alone, though six Member States give the NRA equal or exclusive authority over application of the competition rules in the postal sector. In 21 Member States the NRA and NCA are obliged to provide each other with the information necessary for the application of the Postal Directive and the competition rules in the postal sector and /or regularly consult each other on the application of the competition law to the postal sector.
Main institutional regulatory developments since 2008:
On 10 August 2010 the Commission, on the basis of Article 22 of the Postal Services Directive, and with the full support of Member States and NRAs, established the European Regulators Group for Postal Services (ERGP).
The ERGP serves as a body for reflection, discussion and advice to the Commission in the postal services field. Its task is to facilitate consultation, coordination and cooperation between the independent NRAs in the Member States, and between NRAs and the Commission, with a view to consolidating the internal market for postal services and ensuring the consistent application of the Postal Services Directive in all Member States. The ERGP is an advisory group. Membership is limited to independent NRAs of Member States and the EEA and EU candidate countries participate as observers. Participation takes places at a high level (Heads of independent NRAs) and the chair is elected from the membership. The Commission is an observer and provides the Secretariat. Since it was established, the ERGP has played an important role in postal reform and oversight. Comprehensive information about the ERGP including membership and publications is available here:
http://ec.europa.eu/growth/sectors/postal-services/ergp/index_en.htm
Since 2010, several NRAs have been fundamentally reorganized. In the UK, the Postal Services Act 2011 transferred responsibility for regulation of postal services from the single-sector regulator Postcomm to Ofcom (the regulation and competition authority for the UK communications industries). In the Netherlands, a new regulator, the Netherlands Authority for Consumers and Markets (ACM) was created from a merger on 1 April 2013 of the Netherlands Consumer Authority, the Netherlands Competition Authority (NMa) and the Netherlands Independent Post and Telecommunications Authority (OPTA). In Spain the former postal NRA was merged with other national regulators (electronic communications, energy, media, airports and railways) and the Spanish Competition Authority (CNC) creating the Spanish Markets and Competition Authority (Comisión Nacional de los Mercados y de la Competencia (CNMC)).
2.2.2.Authorisation and Licensing Regimes
Article 9 sets out the types of regulatory regime and the conditions that Member States may impose to ensure the provision of a certain level of postal services. For services outside the scope of the Universal Service Obligation (USO) "Member States may introduce general authorisations to the extent necessary to guarantee compliance with the essential requirements". General authorisations do not require operators to obtain an explicit decision from the NRA before starting to offer the service concerned.
For services within the scope of the USO, Member States may go beyond a general authorisation and introduce more stringent conditions, "to the extent necessary to guarantee compliance and to ensure the provision of the universal service". These requirements may include an individual licensing regime, where providers must obtain permission from the NRA before offering a service. In turn the license may contain specific rights and obligations in line with Article 9(2), for example setting certain standards for quality, availability and performance of services; requiring contributions to the financing of the universal service; and imposing technical or operational conditions.
Concerns have been expressed that authorisation procedures for postal operators have been used to expand regulatory controls and erect barriers to market entry following the abolition of the reserved area, rather than to enable new operators to benefit from full market opening. In some Member States new regulatory requirements have been created as individual licences have been introduced for services which were previously outside the scope for regulatory control. Wherever possible, authorisations should be in the form of general authorisations applicable to all postal operators in order to minimise barriers to market entry and create the least market distortion.
Figure 1: Designated and authorised postal operators and licensing/authorisation procedures (2010-2012)

Source: WIK-Consult, Main Developments in the Postal Sector (2010-2013), p37 and 43.
The chart above shows whether Member States use a licensing regime (indicated by L) or a general authorisation (G) and the number of authorisations granted for 2010, 2011 and 2012. Most Member States continue to use a licensing regime. Ten Member States (BG, CY, EE, EL, ES, HU, IT, LU, MT and PT) continue to maintain licence requirements for the entire USO area, while six additional Member States (AT, DE, BE, FI, FR and SE), require licenses for portions of the universal service area. Since 2008, LT, LV, PL, RO, SI and UK have replaced licenses with a general authorisation. While most Member States have granted more than one authorisation, the number of active operators is lower than the number of licenses.
Ten Member States appear to apply conditions relating to the ‘quality, availability, and performance’ of services provided by authorised postal operators other than designated universal service providers (USPs). Conditions are permitted by the Postal Services Directive, but only if they are not comparable to ‘universal service obligations’ and if they are strictly ‘necessary and justified’ to accomplish some other objective of the Postal Services Directive, such as protecting users. In particular they are subject to the proportionality requirement under Article 9(3).
For example, the current Belgian legislation imposes strict licence conditions on providers of postal services. After two years of operation, operators are required to deliver twice a week and after five years to serve all three regions of Belgium, expanding in line with minimum percentages for population coverage, as well as applying a uniform rate throughout the country. Given that these conditions erect high barriers to entry they appear to protect the USP from competition rather than specifying necessary and justified requirements. In November 2014 the Commission started an infringement procedure against Belgium and addressed a letter of formal notice to the Kingdom of Belgium. A study commissioned by the Belgian Institute for Postal Services and Telecommunications (BIPT), the NRA, confirmed that the above requirements are neither necessary nor justified. In April 2015, Belgium indicated to the Commission that it would bring forward legislative proposals in 2015 to remove these requirements by amending current national legislation.
Eleven Member States appear to have several authorisation conditions which duplicate requirements of other legislation, for example covering the confidentiality of correspondence. In principle the implementation of the PSD should not duplicate conditions which are applicable through other non-sector specific national legislation.
2.3.The Universal Service: Basic Postal Services for All
Article 3 of the PSD requires Member States to safeguard the provision of certain basic postal services (the “universal service”). This is key to ensuring reliable and affordable postal services for all users across the EU. As a minimum, Member States must ensure a universal service that provides for the collection, sorting, transport, and distribution at least five working days per week of (i) postal items weighing up to 2 kilograms and (ii) postal packages up to 10 kilograms, as well as services for registered items and insured items in both categories. Within these boundaries Member States have flexibility to decide what exactly constitutes a universal service to fit their domestic circumstances. The universal service covers both national and cross-border services (Article 3, paragraph 7). Cross-border postal services are specifically addressed in section 2.8 whereas the focus of sections 2.3 to 2.7 is primarily domestic (universal) postal services.
Many commonly used postal services are not part of the universal service, even where they are provided by the universal service provider. Such services include for example value-added services like track and trace capability or delivery within a specified time window. Other services such as bulk mail or periodicals are part of the USO in some Member States, but not in all.
2.3.1.Designation of Universal Service Provider(s)
The provision of the universal service must be ensured by Member States using one or more of three mechanisms: market forces; the designation of one or more undertakings to provide different elements of the universal service or to cover different parts of the territory; or the public procurement of universal services (Article 4 (2)). Member States are to determine themselves the "most efficient and appropriate" mechanism while respecting "the principles of objectivity, transparency, non-discrimination, proportionality and least market distortion necessary to ensure the free provision of postal services in the internal market", taking into account national needs and conditions.
Directive 2008/6/EC changed the historic preference for the designation of a particular operator, to encourage greater competition and choice in postal services. Nevertheless, all Member States still designate a single universal service provider (USP), with the exception of Germany, which in principle relies on market forces for the provision of the universal service. In all Member States the universal service provider is the historical public postal operator or its corporate successor.
Reliance on market forces requires the least regulatory intervention, but there may be grounds to justify one of the other solutions. Designating a universal service provider (USP) also has implications beyond the provision of the universal service. For example, the different legal status that results from the designation can trigger different VAT treatment (for a certain limited scope of postal items).
To prevent undue distortions Article 4(2) PSD states that any entrustment should be used proportionately that is, only to the extent objectively necessary to ensure the universal service and should be ‘based on the principles of transparency, non-discrimination and proportionality’, while taking into account that the duration of this designation should provide a sufficient period for return on investments. When Member States conduct the periodic review required by Article 4(2) they will need to engage in an objective, transparent, and non-discriminatory analysis, as stated by Recital 23, and to consider carefully if continued reliance on a historic designation model is appropriate or necessary.
2.3.2.Services Provided under the Universal Service Obligation
There is flexibility in the services that can be provided under the universal service obligation (USO) providing that Member States ensure a universal service that provides for the collection, sorting, transport, and distribution of (i) postal items weighing up to 2 kilograms and (ii) postal packages up to 10 kilograms, as well as services for registered items and insured items in both categories. There is therefore significant variation in how Member States define the universal service obligation and the services that are included within the universal service obligation have changed over time. All Member States include single piece letters and parcels. Eleven member states (c. 56% of the EU/EEA letter post market) include only single piece items, while others also include bulk letters (potentially including bulk mail, direct mail and periodicals), bulk parcels and other items.
Table 1: Variations in the Scope of the Universal Service Obligation (2013)
|
Scope
|
Number
|
Member State
|
|
Single Piece Only
|
9
|
BG, CZ, DE, EE, HK, LT, NL, PL, UK.
|
|
Single Piece and Bulk Letters
|
7
|
EL, FR, IT, CY, LV, SE, SI.
|
|
All
|
11
|
AT, BE, DK, ES, HU, IE, LU, MT, PT, RO, SK.
|
Source: ERGP, Report on the Benchmarking of the universal service tariffs, ERGP (14) 23, 2014
There appears to be a trend towards a narrower scope for the universal service obligation. Fewer Member States now include bulk letters, direct mail and periodicals than previously, though more now include bulk parcels in the universal service obligation.
The designation of services as part of the universal service obligation requires a set of obligations stemming from the Directive to be fulfilled. The broader the range of services included in the universal service, the broader the responsibility of the Member State to ensure cost-orientation, non-discrimination, transparency, service quality, etc.
The Directive currently provides for NRA tasks regarding non-universal postal services in three areas: complaints, statistics, and supervision of the regulatory accounts of USPs. Article 19 requires Member States to ensure that all postal operators, i.e. not only universal service providers, maintain certain measures to protect the rights of users. Article 22a that was introduced by Directive 2008/6/EC requires all postal services providers to provide information for clearly defined statistical purposes and to ensure conformity with the Postal Services Directive to the NRA. Article 14 provides that USPs must account for common costs incurred in providing universal and non-universal postal services (in order to be able to check for any cross-subsidies).
As bulk postal services have in more and more Member States been excluded from the universal service obligation, the NRAs’ authority to control pricing in bulk postal markets has receded. However, as outlined in section 3.2.2, in most Member States the universal service provider faces little effective competition. If these products and services are no longer subject to a sector specific regulatory regime, a universal service provider may be able to block market entry, for example by denying access to elements of the postal infrastructure or denying competitors non-discriminatory access to downstream services ("last mile delivery").
Ongoing monitoring is needed to ensure that the provisions in the Directive which protect competition in the universal service area remain sufficient as postal services evolve. Further statistical information for non-universal parcel services and increased regulatory oversight of cross-border services, given the growing importance of parcel delivery for e-commerce, are areas of particular focus.
2.3.3.Frequency of the Universal Service
Article 3 specifies that the universal service should be guaranteed not less than five working days a week save in circumstances or geographical conditions deemed exceptional. Most Member States guarantee the collection and delivery of letters and parcels on five working days, though some exceed this requirement, some for letters and some for both letters and parcels. Some USPs choose to delivery more often than they are formally required to do, for example in Germany where there is delivery on six days but the legal requirement for five. The table below sets out delivery frequencies.
Table 2: Collection and Delivery Frequencies for the Universal Service Obligation
|
Collection and delivery frequency
|
Member State
|
|
5 days for letters not specified for parcels
|
CY, SE,
|
|
5 days for letters, 5 days for parcels
|
AT*, BE, BG, ES, CZ, EE, FI, EL, HK, HU, IE, IT, LV, LT, LU, NL, PL, PT, RO, SK, SI,
|
|
6 for letters, 5 for parcels
|
DK, UK
|
|
6 for letters, 6 for parcels
|
FR, DE, MT
|
* In Austria newspapers are delivered 6 days a week and all other products on 5 days.
Source: WIK-Consult, Main Developments in the Postal Sector (2010-2013) and ERGP, (14)23 Report on the Benchmarking of the Universal Service Tariffs updated
The importance the Directive attaches to the delivery frequency and thus also the limits to the derogation relating to circumstances or geographical situations deemed exceptional has been reflected in the wording of Recital 21 of Directive 2008/6/EC, which states explicitly: "The universal service guarantees, in principle, one clearance and one delivery to the home or premises of every natural or legal person every working day, even in remote or sparsely populated areas." Therefore, it is clear that any derogation granted by the NRA in accordance with Article 3(3) of the Directive must be based on clear and objective criteria and be subject to regular monitoring as to its scope and effects.
The possibility to provide exemptions from the minimum obligation due to exceptional circumstances or geographical conditions has to date been used in a restricted manner, as was the Directive's intention. 16 Member States apply the derogation as allowed under Article 3(3) of the Postal Services Directive but most exceptions are limited to the exclusion of less than 1% of the population from daily home delivery. An ERGP study on best practice recommended that exemptions should be based on objective and published criteria, monitored regularly and subject to control mechanisms.
Main developments:
From 1 January 2014 Post NL reduced the number of collection and delivery days from six to five. Reductions were also proposed to the number of post boxes and postal agencies required.
In Denmark the law allowed in 2014 for the universal service provider to change the delivery frequency so that first class letters are not delivered to private households on Mondays (only Tuesday-Saturday).
Posti (then Itella) in Finland conducted a trial in autumn 2014 where it delivered non-USO products four days a week while continuing to deliver USO products five days a week. Delivery routes were also changed. Following the trial, 70% of recipients felt that delivery was working well and 80% thought that the mail delivery was normal. Almost two thirds were ready to see the delivery model expanded permanently to the rest of the country.
2.3.4.Studies on User Needs and the Universal Service Obligation
Given the ongoing decline in letter post volumes, and the increasing accessibility and use of e-commerce, some Member States (and other organisations) have conducted reviews of the USO and user needs.
Studies include:
A 2010 study commissioned by the Irish NRA ComReg observed a diminishing importance of letter post and the use of electronic substitutes among residential customers and SMEs. In contrast, large businesses, governmental bodies and NGOs still relied on letter post. Both residential and organisational customers emphasised the importance of delivery to every address and the reliability of the service (i.e. at the same time of the day). Residential customers and SMEs were found to have lower requirements that the universal service specified, but customers were rather dissatisfied with service quality in terms of parcels.
In 2012 Michel Barnier, the former Commissioner for the Internal Market and Services, used the “Postal User Forum” as a forum for a debate between postal users and various stakeholders (including mail-and parcel users, on-line retailers, internet service providers, postal and courier operators) to identify today's needs and experiences on mail and parcel delivery and solutions for the future. The service levels of the universal service definition were questioned by stakeholders in different contexts, including the context of digitalisation and letter volume decline.
A 2012/13 Ofcom study
concluded that the postal market was meeting the reasonable needs of users in the UK although tolerance of changes to the universal service was quite high. Users wanted more convenient delivery of parcels. When questioned about possible future scenarios, residential customers were willing to consider a single tier postal service, slightly more expensive than current second class but quicker, a reduction in frequency from six to five days and greater flexibility in delivery/collection times. Customers were willing to accept significant changes in the service in order to maintain prices. They were not willing to have differences in local and national services.
The ERGP published a discussion paper which set out the key challenges and held a public consultation on the universal service obligation in view of market developments in autumn 2014.
Many of those who responded to the consultation called for a reduction in the scope of the USO, at least at the European level, in order to give Member States greater flexibility given the nature of their domestic letter markets.
ERGP work in this area is continuing in 2015.
2.3.5.Tariffs for Universal Service Products
Article 12 of the PSD requires universal postal services to be affordable for all users, prices to be cost-oriented and transparent and provision to be on a non-discriminatory basis. Member States have a certain margin of discretion as to how to interpret these principles. All Member States apply some form of price control and most Member States have included the principles in their national postal legislation.
The aim of affordability is to ensure basic postal services are within everyone's means. In some Member States the existence of a price cap is deemed sufficient to ensure affordability, though in some cases affordability is tested, for example by regulatory approval of price changes, multi criteria assessments and consultations. Some regulators publish the results of their affordability tests.
Comparisons of 'affordability' across Member States need to take into account the impact of exchange rates, standards of living and the domestic postal product mix. To compare affordability, the ERGP used a range of measures which showed that for single piece 20g domestic priority letters, Latvia was the most expensive and Malta the cheapest of the 26 Member States that were included in a survey using a daily net earnings comparison. Using the published price at adjusted exchange rates and excluding VAT, Latvia (EUR 1.22) was the most expensive and Malta (EUR 0.35) was the cheapest again. The size and weight categories and their corresponding prices were however not always compatible, for example Poland's first weight category is for letters up to 350 grams rather than 20 grams, and some Member States also offer cheaper 'non-priority' alternatives.
Figure 2: Domestic letter price (20g, priority) as proportion of daily net earnings (‰)

Source: ERGP (14) (23) ERGP Report on the benchmarking of the universal service tariffs.
For a heavier weight category, a domestic priority letter weighing up to 500g using adjusted exchange rates, Italy (EUR 5.18) was the most expensive and Cyprus (EUR 0.75) the cheapest Member State. When compared to daily net earnings, Romania was the most expensive and Luxembourg the cheapest.
For a domestic single piece 2kg parcel, Sweden (EUR 13.47) was the most expensive and Denmark (EUR 1.06) the cheapest, adjusted for exchange rates. Compared to daily earnings, Denmark was the cheapest and Hungary the most expensive.
Figure 3: Domestic letter price (20g priority in 2013) using purchasing power parity
Source: European Commission Postal Statistics, own calculations on the basis of the prices of 2013
In terms of affordability, PPP prices in the eastern Member States appear to be higher than prices in the southern or western Member States, although when comparing nominal prices the exact opposite is observed.
Average price trends in EU28 show an average price increase for 2012 to 2013 of 5.4% that is distributed unevenly across Member States. In southern Member States higher price increases are observed compared to the eastern or western ones.
To help compensate for declining volumes, some universal service providers have significantly increased their basic tariffs in recent years, including in Denmark, Estonia, Luxembourg, Hungary and the UK, though in many cases these Member States previously had postal tariffs that were stable or declining in real terms. For example in Estonia, in the first price change since 2011, Eesti Post announced a 22% increase in the cost of sending a domestic standard letter from 1 September 2014 and the price of all universal services (including international letters and parcels up to 20kg) also rose by 18% on average. In Southern and Eastern Member States between 2010 and 2012 tariffs usually remained stable or declined in real terms, though since then some universal service providers have announced notable increases, including Malta Post and Poczta Polska.
Non-priority letter services allow for more flexibility in postal operations and are a way to reduce network cost and help mitigate declining volumes as well as ensuring the continued availability of an affordable service. In around half of the Member States USPs offer non-priority basic letter post services that are delivered the second or the third day after posting (second fastest standard category: SSC), rather than on the next day. In 2011 Austrian Post launched an economy/ D+3 service for business customers, having previously offered only a next day service. La Poste (France) has also introduced a D+2 letter (‘lettre verte’) for consumers and business customers additional to its D+1 service (‘lettre prioritaire’) and D+3/4 service (‘l’écopli’). In Denmark, the UK and Hungary tariffs for second class letters have increased substantially less than those for first class letters, in order to help maintain the affordability of basic services. In Denmark and the UK the second class letter is still subject to ex ante price regulation while the first class letter is not. The price difference between first and second class letters in most Member States is more than 10% and can be as large as 37.5% (Romania).
The cost-orientation requirement aims not only to prevent prices of basic postal services from being too high, but also to prevent pricing below service specific costs, which could restrict competition and could therefore lead to higher prices in the long run. NRAs measure and test cost-orientation in different ways, for example by scrutinising individual prices, the price of a level of service (i.e. counting the different size or weight steps) or the price of a basket of services, and using regulatory and financial accounts. To test the principle of cost-orientation, some NRAs regard price caps as sufficient, while others monitor specific criteria for cost-orientation or perform other tests, primarily using either the regulatory or financial accounts of the USP. Stakeholders other than the USP are usually not involved and the results of these tests are rarely published.
ERGP analysis of the determinants of pricing found that around 20% of the observed difference in letter prices is due to population density. The correlation between price and degree of urbanisation was not statistically significant but the relationship with dwelling type (detached houses, flats etc) was significant. Labour costs accounted for 36.7% of the variation in prices.
Most Member States ensure transparency by requiring the USP to publish prices, in line with the European Committee for Postal Regulation's (CERP) recommendation, although around half do not have defined criteria for 'transparency'. A small number go further than publication alone, for example by requiring pricing models to be submitted to the regulator, requiring the publication of pricing principles and/or the disclosure/publication of individually negotiated prices. Some USPs also publish tariffs outside the scope of the universal service and some publish information in other languages.
The aim of the principle of non-discrimination of tariffs is that customers in comparable conditions should be able to benefit from equivalent tariffs and conditions. A wide range of potential criteria can be used to define non-discrimination, e.g. geographical distribution, volumes, levels of pre-sortation, or access for certain user groups. NRAs in almost all Member States take steps to ensure non-discriminatory tariffs with the exception of Hungary. Non-discrimination is usually tested through ex-ante instruments or ex-post testing. There have been a number of legal cases related to the principle of non-discrimination, see section 2.11 for further details.
2.3.6.Price Regulation
Ex ante approvals can help to ensure that prices of universal services are cost oriented and are therefore necessary where emerging competition might be damaged by universal service providers setting unreasonably low prices or consumers of universal service products or services might be damaged by universal service providers setting unreasonably high prices. On the other hand, the administrative burden of ex ante price regulation is relatively high and postal operators have limited commercial freedom under such a regime. Certain studies suggest that in a market with declining volumes in particular, some degree of pricing flexibility and a lighter touch regulatory regime may be more likely to meet the aims of affordability and competition than price cap regulation.
Member States use both ex ante and ex post price control methods, though to different extents. The majority rely more on ex ante price regulation than on ex post control. Single piece postal items (letters and parcels) are the items most often subject to ex ante control. Price caps are also used in many Member States, again most commonly on single piece items. Several Member States apply other price control measures in addition to ex ante approvals and price caps, for example checking (ex post) the prices subject to a cap. Even where price controls are not currently used, NRAs may have the power to introduce or extend them, in the event that they are deemed necessary in the future.
Table 3: Products Subject to and Methods of Price Regulation
|
|
Single piece letters
|
Bulk letters
|
Direct mail
|
Newspapers magazines
|
Non-priority correspondence
|
Single piece parcels
|
Bulk parcels
|
|
Ex ante approval
|
AT, BG, CY, EL, ES, IE, LT, LU, LV, MT***, RO, SI, SK
|
AT, CY, EL, LU, LV, MT*** RO, SK
|
AT, CY, EL, MT*** RO, SK
|
AT, EL, FR, MT***, RO, SI
|
BG, EL, LT, LV, RO, SK,
|
AT, BG, CY, EL, ES, LT, LU, LV, MT*** RO, SI, SK
|
AT, EL, MT***, RO, SK
|
|
Price cap
|
AT, BE, DE**, EE, FR, HU, IE, IT, NL, PL, PT
|
FR, IE, IT, PT
|
FR, PT
|
IT
|
BE, FR, HU, PL, UK
|
BE, EE, FR, IE, IT, NL, PL, PT
|
FR
|
|
Ex post control
|
DK, FI, HU, SE
|
DE, ES, SE
|
DE, DK, SE
|
DE, SE, SK
|
DK, FI, SE
|
DE, DK, FI, HU, SE
|
DK, ES, HU, SE
|
Source WIK-Consult, Main Developments in the Postal Sector (2010-2013), p141
Main developments:
In 2011 Bundesnetzagentur (BNetzA), the German NRA, deemed the tariffs of Deutsche Post’s (fully owned) subsidiary First Mail to be discriminatory and anticompetitive. First Mail offered regional letter services for business customers using separate delivery to that of Deutsche Post in densely populated areas in Germany and in competition with other postal service providers. The other operators accused First Mail of setting prices too low and hindering competition. In its decision, the NRA concluded that prices offered by a subsidiary of a regulated firm cannot be assessed separately from the parent, and that Deutsche Post and its subsidiary should be considered as one entity. First Mail was therefore obliged to set prices no lower than prices for downstream access at the inward mail centre of Deutsche Post. Following the BNetzA decision, Deutsche Post ended First Mail’s operations at the end of 2011.
In April 2012 the UK NRA, Ofcom, substantially reduced the scope of ex ante price regulation. The goal was to give Royal Mail greater pricing flexibility in order to sustain its financial viability and ensure the provision of universal service in view of changing market conditions. Next day ('first class') letters and downstream access prices are no longer capped. To protect the affordability of universal services for elderly people and low income customers in particular, Ofcom maintained a "safeguard" cap on prices for second class mail (two to three day delivery) only.
The Commission for Communications Regulation (ComReg), the Irish NRA, introduced a price cap for the universal service in 2014. This is the first time the Irish USP, An Post, has been subject to a price cap control. The price cap is effective for five years and sets an upper limit on the amount that An Post can charge, rather than setting actual prices. The cap is indexed to the consumer price index, minus an adjustment to encourage the efficient provision of postal services.
In Portugal, the NRA issued a decision in 2014 on the criteria for setting universal service prices which will be applied from 2015 until 2017. Correspondence, editorial mail and parcel basket of services are controlled by a price cap, as well as legal summons and notifications service. For all other universal postal services, CTT has to notify the NRA of prices to be introduced at least 30 days ahead of the date on which prices take effect and show it complies with the tariff principles (affordability, cost-orientation, transparency and non-discrimination) and pricing criteria defined in the decision. If the NRA deems the proposed prices do not comply with the principles and criteria the USP is notified based on a substantiated decision, so that company may revise such prices within 15 days. If on the other hand the NRA remains silent, then the USP is entitled to introduce the notified prices (when the notification period has elapsed).
In France ARCEP approved higher limits for price changes (concerning the price cap period from 2013 to 2015) than in previous price cap periods due to expected falling revenues of the regulated services. Following a subsequent review in light of declining mail volumes, La Poste and ARCEP implemented a new pricing framework equal to the consumer price index increased by 3.5 points a year on average for universal service prices. La Poste announced an average price increase of 7% for mail from 1 January 2015.
2.4.Financing the Universal Service Obligation
2.4.1.Regulatory Accounting
Article 14 requires universal services providers to keep separate accounts for universal service and non-universal service products and NRAs to ensure compliance with the cost allocation principles set out in the Directive. The primary aim is to require accounts to be kept that can be used to determine any net cost or unfair financial burden created by the universal service, though separate accounts can also help the NRA to determine whether the USP is acting according to the tariff principles set out in Article 12 and, for example, not engaging in discriminatory pricing.
In the majority of the Member States, regulatory accounts cover non-universal services or even non-postal services (such as unaddressed items or financial services), as well as the universal service area. This fits with the totality principle identified by the ERGP that the regulatory accounts should cover any activity that is used by both universal services and non-universal services.
The main cost basis that is used for regulatory accounting is historical costs (as opposed to current costs which are used only in Finland). Most NRAs use activity based costing. The ERGP has clarified that activities should be based on causality, but the USO should not be regarded as a cost driver without being fully evidenced by the USP and agreed by the NRA.
Given that the postal infrastructure is used for both USO and non USO products, the correct allocation of joint costs and common costs is vital. NRAs use different methods for common cost allocation which may, but need not be, based on activity based costing. The most widespread methodology seems to be equi-proportional mark-up (EPMU) which allocates all common costs according to their proportion of total costs and is therefore consistent with Article 14(3)(b)(iii). EMPU does not however reflect how common costs are actually incurred. The long run (average) incremental cost (LRIC) approach may be more accurate and are used in addition or instead of EPMU in several Member States.
In general, cost allocation methods are not public. Few NRAs publish which cost allocation method they use and the structure of regulatory financial reporting also tends not to be public. The NRAs in France and the UK have however published templates for their regulatory cost accounts.
In May 2013 the European Regulators Group for Postal Services (ERGP) published a common position on cost accounting rules. This followed an earlier ERGP report and public consultation in 2012.
2.4.2.Net Cost of the Universal Service Obligation
According to the 2008/06/EC Postal Services Directive, "Member States should be given further flexibility to determine the most efficient and appropriate mechanism to guarantee the availability of the universal service, while respecting the principles of objectivity, transparency, non-discrimination, proportionality and least market distortion necessary to ensure the free provision of postal services in the internal market". In this context the Postal Services Directive recognised that "the external financing of the residual net costs of the universal service may still be necessary for some Member States." The 2008 Directive therefore introduced Annex 1, Guidance on calculating the net cost, if any, of the universal service.
Annex I of the Postal Services Directive provides the general methodological framework for calculating the net costs of the Universal Service Obligation (USO). The details of the calculation and the methodological alternatives available however, are not dealt with by the Directive.
The European Commission commissioned a study in 2012 to evaluate how Member States have assessed the net costs of the universal service obligation to date. At the same time, the European Regulators Group for Postal Services (ERGP) had been conducting related research in this field. There are also a number of state aid decisions already adopted by the European Commission concerning postal operators which apply Annex I to calculate the net cost of the universal service obligation.
Following previous studies and relevant case law and in line with its obligation to provide assistance (Article 23a), an Annex to this Report is included that sets out different approaches to calculate the net costs of the Postal Universal Service Obligation that have been found to be consistent with Annex I of the Postal Services Directive.
The estimated cost of the universal service in western Member States has been estimated to be around five per cent of the overall cost of the USO, whereas in the eastern Member States it is thought to be much higher and in the region of 30% to 70%. There is also some evidence the net cost of the USO is increasing over time, particularly given falling mail volumes.
Article 7 of the Directive provides mechanisms in the event that any net cost of the universal service obligation represents an unfair financial burden on the universal service provider. The alternative mechanisms are compensation from public funds (i.e. general taxation) or a cost-sharing mechanism, potentially a compensation fund "for the sharing of the net cost…between providers of services and/or users."
Several Member States have deemed the universal service obligation to be an unfair burden. Some Member States (including IT and PL) compensate the universal service provider through public funds and others (CY, EE, HK, IT and SK) have established a compensation fund, although a further 18 have authorised the use of a compensation fund. Concerns have been raised that the establishment of a compensation fund could create a barrier to entry, and developments in this respect will need to be closely monitored.
2.5.Access to Postal Services, Network and Infrastructure
2.5.1.Access Points
Article 3(2) requires Member States to ensure that the density of the points of contact and access points takes account of the needs of users, including where appropriate a minimum number of services at the same access point and an appropriate density of access points to postal services in rural and remote regions. Access points are physical facilities, including letter boxes and the premises of the postal service provider, such as post offices, where postal items may be deposited into the postal network. Rural postal points can provide an important infrastructure network for access to electronic communications and e-commerce (for both retailers and consumers).
In 2013 there were around 700,000 post boxes in the EU. In some Member States the number of post boxes has remained relatively stable. In other Member States it has fallen, notably in DK, PT, and PL where the number of post boxes fell by over 10% between 2010 and 2013. Germany is the only Member State where there is a significant number of street letter boxes for other operators as most business customers who use providers other than the USP for bulk mail services in other Member States will have mail collected directly from their premises rather depositing it in a post box or at a post office. Not all Member States have legal requirements specifying a minimum number of post boxes.
In 2013 there were about 145,000 post offices (of USPs) in Member States. Numbers have continued to decline slightly: by 1.6% since 2010 compared to an average of 1.1% between 1998 and 2007 for the EU 25, and by 0.3% between 2012 and 2013. In some Member States, however, the decline has been significantly higher, for example in Estonia, Portugal and the UK.
The nature of access points/post offices is evolving alongside changes in the product mix. Some Member States have reduced their post office networks as letter volumes have fallen and government and other services (e.g. bill payment) have moved from over the counter services to online transactions. The agency model of post office provision has become more popular as it spreads costs over a wider product offering which can also drive footfall (e.g. AT, FR and PL). Some Member States already had a high share of agencies, though others have retained full ownership of the network, perhaps in some circumstances due to the provision of financial services requiring increased security alongside a traditional postal offering.
Parcels also provide opportunities for post offices and other retailers, as customers become more willing to have their parcels delivered to locations other than their homes, or legislation is passed which permits this. In some instances post office opening hours have increased to offer more convenient parcel collection (and sending) times, offering a better service to customers. Retail networks and/or customer collection points are also being developed by other postal operators as express operators and other parcel delivery companies seek to establish a consumer-facing presence.
In 2012 UPS bought Kiala, a network of collection points inside retail outlets. UPS have expanded the network under UPS branding and there are now over 13,000 collection points in nine Member States.
DHL's Packstations are machines that allow customers to collect and return packages 24/7. There are 2,750 packstations in over 1,600 locations in Germany and they are being installed in other European countries. DHL also have a physical presence in other EU markets, through for example through DHL Service points (of which there are 45,000 worldwide).
InPost offers click and collect parcel lockers which offer 24/7 tracked delivery. They operate in 22 international markets with over 3,500 parcel terminals.
2.5.2.Access to Postal Infrastructure
The Third Postal Directive introduced, in Article 11a, a requirement for Member States to ensure transparent, non-discriminatory access conditions to certain elements of the postal infrastructure or services within the scope of the universal services such as address databases, post office boxes, delivery boxes, change of address information and redirection services and return to sender services. Access to such facilities is becoming increasingly important given competition in the postal sector and the contemporary uses of postcode and address services such as navigation systems and personalised transport timetables. The table below summarises the types of access offered.
Table 4: Access to Postal Infrastructure
|
Type of access
|
Member States
|
No answer
|
Number
|
% survey market
|
|
Access to post codes
|
AT*, BE*, BG, CY, CZ, DE*, DK, EE, FI, FR, HU, LT, LU, MT, PL, SE, SI, UK
|
|
18
|
78%
|
|
Access to post office boxes
|
CY, CZ, DE, DK, EE, FR, IT, LT, LU, LV, MT, NL, PL, SE, SI
|
AT, IE, HR
|
15
|
59%
|
|
Access to delivery boxes
|
AT, BE*, BG, CY, DE*, DK, ES, FR, HU, IE, IT, LT, LU, PL, PT, SK
|
HR
|
16
|
65%
|
|
Access to address database
|
CY, CZ, DE, DK, EL*, FR, LT, LU*, SI, UK
|
AT, IE, HR
|
10
|
64%
|
|
Access to change of address database
|
AT, CY, CZ, DE, DK, EL*, FR, LT*, LU*, SI
|
IE, HR
|
10
|
47%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Access to USP redirection and return services
|
CZ, DE, DK, EE, EL*, FR, LT, LU, MT, SI
|
IE, HR
|
10
|
43%
|
* indicates different answers by USP and NRA.
Source: WIK-Consult, Main Developments in the Postal Sector (2010-2013), p45. Percentage of survey market includes EEA countries surveyed.
In around half the Member States there is access to no more than two elements of the postal infrastructure. Given new innovations in the sector (such as dedicated parcel delivery boxes) it will be even more important that NRAs have the powers and regulatory instruments to assure access to elements of the postal infrastructure wherever necessary to protect the interest of users and/or to promote effective competition.
Main developments include:
Section 34 of the Postal Market Act in Austria came into effect on 1 January 2011. This required all postal service providers to be able to access letter and curbside delivery boxes, including those within buildings. Previously only the universal service provider, Oesterreichishe Post AG, had been able to access all letter boxes. Following a decision of the constitutional court in 2012 letter boxes were exchanged for ones which can be accessed by all operators.
In Slovenia information on postcodes and address databases was only available in paper format until the end of 2012. The information is now available electronically.
The ERGP held a public consultation on access to the postal network and infrastructure in 2012. The aim was to identify different approaches rather than recommending one particular model for all Member States. For access to infrastructure the report found that there was no widespread detailed regulation of access, with national legislation tending to establish principles and detailed arrangements resulting from negotiation between parties. Nevertheless, even in the absence of a legal obligation, operators tended to offer access to the network.
2.5.3.Access to the Postal Network
Article 12 of the Directive allows USPs to conclude individual tariffs with users, provided that such tariffs and their associated conditions are transparent and non-discriminatory and are available to all users posting under similar conditions. Member States are not obliged to require their USPs to provide access to their network in this way, though most who offer some form of access do legally require the USP to offer this service. In Member States where it is offered, access mail can constitute a significant proportion of mail volumes.
There are different stages at which USPs can provide access to their network and the associated special tariffs. These are summarised in the diagram below. Bulk mail access points allow access for business users with middle sized volumes (with restrictions on permissible amounts). Alternatively the USP - or its competitors - can collect mail directly from business customers. Where permissible, consolidators or other competitors can then deposit mail into the USP's network for local distribution and delivery. This usually requires much larger volumes and a higher degree of sorting that mail deposited with the USP for outward processing. In Germany, France and the UK most of the 'access' volumes come from consolidators and competitors, rather than business customers (as they do in Belgium).
Figure 4: Structure of Access Operations

Source: WIK-Consult
Almost all Member States' universal service providers offer special tariffs. Special tariffs are common for bulk parcel services and direct mail, as well as bulk letter services. Discounts are usually offered for volume and/or the level or preparatory work, such as pre-sorting. They are also sometimes offered for early drop-off times or deposits of deliveries notified in advance.
Table 5: Access to Special Tariffs
|
|
Bulk Letter Mail
|
Direct Mail
|
Bulk Parcels
|
|
USP offers special tariffs?
|
AT, BE, BG, CY, DE, DK, EE, EL, FI, FR, HU, IE, IT, LT, LU, MT, NL, PL, PT, RO, SE, SI, SK, UK
|
AT, BE, CY, DE, DK, EL, FR, HU, LU, NL, PL, RO, SE, SK, UK
|
AT, BE, BG, CY, DE, DK, EE, EL, HU, LU, NL, PL, PT, RO, SE, SK, UK
|
|
|
NA: ES, HR
|
NA: BG, CZ, EE, ES, FI, IE, IT, LT, PT, SI
|
NA: CZ, ES, FI, FR, HR, IE, IT, LT
|
|
Transparent and non-discriminatory?*
|
AT, BE, BG, CY, DE, DK, EE, EL, FI, FR, HU, IE, IT, LT, LU, MT, NL, PL, PT, RO, SE, SI, SK, UK
|
AT, BE, CY, DE, DK, EL, FR, HU, LU, NL, RO, SE, SK, UK
|
AT, BE, DE, DK, EE, EL, HU, LU, PL, PT, RO, SK
|
|
|
|
|
NA: BG, SE, UK
|
|
Available to consolidators?*
|
AT, BE, BG, DE, DK, EE, EL, FI, FR, HU, IE, IT, LT, LU, MT, PT, RO, SE, SI, SK
|
AT, BE, DE, DK, EL, FR, HU, LU, NL, RO, SE, SK, UK
|
AT, BE, BG, CY, DE, DK, EE, EL, HU, LU, NL, PL, PT, RO, SK
|
|
|
NA: UK
|
|
NA: BG, SE, UK
|
|
Available to other postal operators?*
|
AT, BE, BG, DE, DK, EE, EL, FI, FR, HU, IE, IT, LT, LU, MT, NL, PT, RO, SE, SI, SK, UK
|
AT, BE, DE, DK, EL, FR, HU, LU, NL, SE, SK, UK
|
AT, BE, BG, DE, DK, EE, EL, HU, LU, NL, PL, PT, SK, UK
|
|
|
NA: UK
|
|
NA: SE, UK
|
* required by law and/or verified in practice
Source: WIK-Consult, Main Developments in the Postal Sector (2010-2013, p49
Transparent and non-discriminatory access to special tariffs is required by law and verified in practice by most Member States. How Member States verify the application of these principles does however vary significantly, for example Belgium requires publication whereas others including Sweden and the UK do not. Special tariffs are not available to consolidators or other postal operators in a few Member States.
Developments include:
ACS SA, a provider of courier and postal services for business mailers in Greece, filed a complaint with EETT, the Greek NRA in 2009, alleging that ELTA, the Greek USP had not been transparent and discriminated against ACS SA regarding the downstream access it already provided to its own subsidiary Tachymetafores Elta. EETT fined ELTA in July 2012 for abuse of its dominant position and obliged ELTA to provide non-discriminatory access.
In 2010 bpost (Belgium) introduced price changes which limited discounts for consolidators and mail handlers according to their individual clients' volumes instead of aggregating them (so called "per sender model"). In 2011 BIPT, the NRA, took the view that this new price system (that was not based on the total volume deposited by the intermediaries) was contrary to the postal legislation, based on a previous judgement of the Court of Justice. In parallel bpost was judged by the Belgian Competition Authority to have acted contrary to competition law (Article 102 TFEU) in relation to the same pricing model. bpost appealed against BIPT’s decision to the Cour d’appel de Bruxelles. The latter referred the case to the European Court of Justice (CJEU). In its judgment of 11 February 2015 (C-340/13) the CJEU stated that a model based on quantity discounts per sender is allowed under Article 12, fifth indent of the Directive and that bulk mailers and consolidators are not in comparable situations as regards the objectives pursued by the system of quantity discounts per sender. The referring court has now to decide on the merits; and the competition case on this issue is still pending. Furthermore, the ERGP is examining the possible implications of this judgment for the development of competition on the postal market. It is nevertheless clear that discount models will have to continue to be compatible with Article 12 of the Postal Service Directive and competition law, although the relationship and interdependency between quantitative and qualitative discounts needs to be carefully assessed.
APEK, the Slovenian NRA, ordered Pošta Slovenije in 2010 to provide discounts of 16.8% - 48.4% for access services, following complaints by a prospective consolidator. The Postal Services Act in Slovenia requires the USP to provide access at the request of an alternative postal operator (a provider of interchangeable postal services). Pošta Slovenije does however allege that as a consequence some bulk senders have registered as postal operators themselves in order to benefit from these discounts.
In 2012 PTS, the Swedish NRA, introduced as a licence condition that Posten AB (the USP) publish prices and discounts for universal services products in full on its website. Posten AB appealed this decision.
The ERGP has conducted analysis of the list prices for bulk mail, although they caution that criteria for bulk mail services differ between Member States. Their 2014 report found that the cost-orientation principle is implemented in different ways, including for bulk mail. Bulgaria, Sweden and Malta are the Member States with the lowest bulk mail (letter) prices.
2.6.Quality of Service
Improving the quality of postal services across the EU has been one of the core aims of EU postal reform since its inception. Article 16 requires quality of service standards focussing on routing times, regulatory and reliability to be set and published in relation to the universal service, and to be subject to independent monitoring. Member States have the flexibility to determine standards for domestic post providing they are compatible with those for intra-Community cross-border services which are set by the Directive. Article 18 and Annex II set out the requirements for intra-Community cross border letter mail services: 85% D+ 3. i.e. delivery within three working days after the date of deposit (D) and 97% D+5, delivery within five working days after deposit.
Transit time standards are most common for single piece services. All Member States have transit time standards for single piece priority letters, though only twelve are known to have them for non-priority letters. Routing time standards are more common for single piece parcels than for bulk.
All Member States have a defined domestic D+1 target except Spain which has only a D+3 target. D+1 targets are between 80% and 97%. Transit time data is published in different ways, including special quality reports by NRAs, annual reports of NRAs, USP publications and market studies.
Figures 5: Priority (D+1) Single Piece Letter Services Quality Achieved Against Target by Country 2012/13
 Source: ERGP (14) 23 Report on benchmarking of universal service tariffs, 2014
Source: ERGP (14) 23 Report on benchmarking of universal service tariffs, 2014
Figure 6: Non-priority (D+2 or D+3) Single Piece Letter Services Quality Achieved Against Target by Country 2012/13
 Source: ERGP (14) 23 Report on benchmarking of universal service tariffs, 2014
Source: ERGP (14) 23 Report on benchmarking of universal service tariffs, 2014
Where there are defined transit time targets for national mail, this is measured by universal service providers in accordance with the CEN standard EN 13850 which covers single piece priority mail. Use of standard EN 14508, which covers non priority mail, is less common. Time performance measurement of parcels that is compliant with the technical report TR 15472 takes place only three member states.
Intra-EU post is measured by the International Postal Cooperation (IPC), whose measurement is compliant with CEN EN 13850. In 2014 the average time for mail delivery in Europe was 2.4 days, with 90.6% delivered within the three days of posting and 97.8% within five days, exceeding, for the 17th year, the respective targets of 85% and 97%. Even allowing for a change in the measurement standards which caused an estimated 1% reduction in performance, an adjusted D+3 performance of 91.6% (rather than 90.6%) was nevertheless the lowest performance since 1999 (90.7%). The fall can be explained in part by operators seeking to make efficiency improvements to compensate for falling mail volumes. By way of comparison in 2013 D+ 3 performance was 92.5% and D+5 98.2% and since 2008 D+3 performance has ranged varied between 90.6% (2014, unadjusted) and 94.6% (2008).
If transit time targets for letter post are not achieved, most Member States are able to take corrective action. The reverse is true for parcels where a minority of Member States have the competence to address failures to meet standards for parcels.
One of the six priorities in the annual Union work programme for European Standardisation for 2015 is postal services. The Commission aims to issue a standardisation request concerning the specific features of parcel delivery services and is also considering whether a request for the revision of any existing European standards is needed.
2.7.Protection of Users
Article 19 of the Directive requires Member States to ensure that transparent, simple and inexpensive procedures for dealing with complaints are available from all postal operators, and not only from universal service providers. Where warranted, a system of reimbursement and/or compensation is also required. The universal service provider, and where appropriate other undertakings providing services within the scope of the universal service area, are required to publish the number of complaints they receive and how they have been dealt with alongside the annual report on performance against service standards required by Article 16.
In the reporting period the CJEU (Case C-148/10) ruled that Article 19 must be interpreted as "not precluding national legislation which imposes on providers of postal services which are outside the scope of the universal service a mandatory external procedure for dealing with complaints from users of those services". The case arose from DHL International NV's opposition to mandatory participation in the financing of the external complaints scheme (in this case an ombudsman within the NRA and financed by fees on qualifying undertakings), claiming that the express delivery services it provided were not postal services.
All Member States have extended user protection to cover other postal service providers as well as the universal service provider. Most universal service providers have introduced a system of compensation. Most Member States have appointed a 'competent national authority', usually the NRA or ombudsman, to review complaints that have not been satisfactorily resolved by the USP. Less than half of the Member States comply with the (voluntary) European Committee for Standardisation (CEN) standards EN 14012 for handling complaints and providing redress. Enforcement in over half of the Member States is by the NRA and national consumer protection authority (NCPA), by the NRA alone in just under half of the Member States and the NCPA alone one Member State.
To improve dispute resolution, the Directive also requires Member States to encourage the use of out-of-court schemes. In addition implementation by the Member States of the Alternative Dispute Resolution Directive by mid-2015, the launch of the Online Dispute Resolution Platform in January 2016 will help to encourage cross-border e-commerce.
The ERGP Report, Best practices in the field of consumer protection, quality of service and complaint handling sets out best practices in a range of areas. Noting the diversity of legislative and regulatory frameworks in Member States, the principles focus on transparency and meeting the needs of users. Suggested best practices include research regarding consumer needs, measurement of consumer satisfaction and complaint handling information and procedures.
2.8.Internal Market for Postal Services: the Cross-Border Dimension
2.8.1.Legal Obligations and Regulatory Oversight
Article 3(7) of the Directive clarifies that the universal service covers cross-border and domestic services. Therefore the pricing principles contained in Article 12 of the Directive are to be applied to both national and international services. In addition, Article 13 requires Member States to encourage universal service providers to respect the following principles in cross-border terminal rates (also known as terminal dues or inward land rates in Universal Postal Union (UPU) terminology): cost orientation, remuneration related to quality of service, transparency and non-discrimination. Any deviation from these principles must be restricted to the minimum required and limited to any transitional arrangements while the principles are being implemented. Article 12, covering tariff principles, is also applicable to cross-border services which are part of the universal service obligation or the result of a special tariff. Article 18 and Annex II to the Directive set out specific intra-EU quality of service standards.
A number of aspects of postal services are also subject to regulation by the UPU, a specialised agency of the United Nations. EU law and UPU law overlap to some degree, for example they both address the rates public postal operators can charge each other for cross-border services, the scope of the universal service obligation, the designation of the universal service provider/designated operator, quality of service standards, customs and security and competition. In the UPU it is the individual Member States who represent themselves and conclude agreements. The European Commission gained the status of formal observer in the 2012 UPU Congress in Doha.
Member States declare at UPU Congresses that UPU Acts will be implemented in accordance with Member States obligations arising from the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union in general and the Union acts implementing them, which include the Postal Services Directive. The aim to ensure consistency between the regulatory regimes and the full respect of EU law is not limited to aspects contained directly in the postal acquis but extends also inter alia, to customs and security controls.
Almost all NRAs oversee both intra- and extra-EU postal services, as well as domestic ones. Only the Dutch NRA seems to be restricted to intra-EU matters.
2.8.2.Tariff Principles
As noted above, Article 13 of the Directive requires Member States to encourage universal service providers to reflect the principles of cost orientation, remuneration related to quality of service, transparency and non-discrimination for their cross-border transactions within the EU. Evidence does however suggest that NRAs monitor USPs' application of these principles less closely for cross-border prices that they do for domestic ones.
Most European universal service providers are parties to the REIMS V agreement, which sets terminal dues among participating European operators, and came into force in 2012. On 23 October 2003 the Commission adopted a decision under EU competition rules, notably Article 81 EC Treaty (now Article 101 TFEU), prolonging for an additional five years the exemption of the REIMS II agreement under EU competition rules subject to a condition that non-discriminatory access to REIMS terms and conditions would be provided to third parties. Following the adoption of Regulation 1/2003 and modernisation of EU competition rules, the parties to an agreement have to ensure its compliance with EU competition rules ("self-assessment" mechanism).
Concerns about whether cross-border parcel prices are affordable arise from the frequent number of surveys of both customers and e-retailers that cite the high cost of cross-border delivery and returns to be a barrier to e-commerce: the most common difficulties companies encounter when selling online to other countries are related to their costs for delivery. Companies already selling online (cross-border) are concerned that delivery costs are too high (51%), that guarantees and returns are too expensive (42%), and that resolving complaints and disputes cross-border are too expensive (41%). Companies that don’t sell online, but are currently trying to do so, are more likely to cite these problems, with 62% having concerns that delivery costs are too high, 62% that resolving complaints and disputes cross-border are too expensive and 58% that guarantees and returns are too expensive. High cross-border deliveyr costs and high return shipping costs are the top two concerns with buying cross-border, each being mentioned by around one quarter or respondents. Several studies and the Commission's own research indicates that the list prices for single-piece products are often two to five times higher than the prices for domestic delivery.
High prices are commonly attributed to low volumes and lack of bargaining power by low volume senders, typically SMEs and consumers. Low volumes generate a higher cost per item, though on the other hand the higher prices may also reflect weak competitive pressure in the cross-border market segment. Given the growing importance of cross-border parcel delivery, and in the framework of its Digital Single Market Strategy for Europe, the Commission services launched a public consultation on 6 May 2015 and are considering what actions may be needed. This is in addition to the actions already undertaken by the Commission and different stakeholders following the adoption by the Commission in December 2013, of the Roadmap for completing the single market for parcel delivery. See section 3.3.5 for further details.
2.8.3.Customs and Security Controls
Universal service providers also benefit from a number of other advantages in the cross-border dimension compared to other postal operators, for example simplified customs procedures. The Universal Postal Union governs such procedures which are the same for all countries and not available to other providers of postal services
The Union Customs Code (UCC) was adopted on 9 October 2013 as Regulation (EU) No 952/2013 of the European Parliament and Council. It entered into force on 30 October 2013 and repealed Regulation (EC) No 450/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 April 2008 laying down the Community Customs Code (Modernised Customs Code). The substantive provisions of the UCC will apply only on 1 May 2016, once the UCC related Commission acts (Delegated and Implementing Acts) (UCC DA/IA) are adopted and have entered into force.
The UCC legal framework, thus established, will limit the current exemptions which postal operators enjoy regarding the requirements for an advance data submission for the purposes of safety and security. Transitional measures will be put in place to allow posts to adjust to these changes.
These rules are also in accordance with the UPU framework. In September 2012, on the basis of a proposal supported by EU Member States and in close coordination with the Commission, the UPU Doha Congress amended Article 9 of the Convention in order to align security controls for postal items sent by universal postal operators with requirements imposed on other comparable flows. The implementation of this general provision by UPU Contracting Parties has however incurred substantial delays though are still on the agenda.
As regards the customs clearance of postal items, the UCC delegated regulation, adopted by the Commission and the current draft UCC implementing act include rules that will allow postal operators to gradually adjust but also to be able to better cope with the large volumes of postal items. A possibility for the lodging of a declaration with a reduced data set is provided.
2.9.Data Collection
Article 22a was introduced in the Third Postal Services Directive to ensure the availability of reliable and up-to-date postal statistics. Member States are therefore required to ensure that postal service providers supply financial information and information on the provision of the universal service, in particular to NRAs where such information is required to ensure conformity with the Directive or for clearly defined statistical purposes. The Article in question, as the Postal Service Directive in general, is neither limited to the scope of the universal service nor to designated postal service providers. This point is increasingly important given the variation in the scope of the universal service, the growing market for parcels and competition in the letter markets which mean that an understanding of the evolution of the postal market as a whole is needed to monitor the sustainability of the sector and in particular the universal service.
Eurostat (which was the main information point for postal statistical information) decided in 2013 to terminate data collection on postal services. From 2014 the Commission Directorate-General for the Internal Market, Industry, Entrepreneurship and SMEs has assumed the role of compiling statistics at the European level. This data is collected using a slightly different methodology to Eurostat, so some sections of this Staff Working Document include two tables, one showing figures up to 2011 (from Eurostat or other sources) and another for 2012 and 2013 (using data collected by the European Commission). 2013 is the most recent year for which postal statistics are available, whether produced by the European Commission or the Universal Postal Union. The Commission statistics are collected in collaboration with NRAs, who receive the data only after universal service providers publish their accounts. Data is then validated and complied at the EU level.
Overall, Article 22a has been implemented with respect to data for ensuring compliance with the Directive (clause 1a). Some NRAs do however still lack the authority to obtain certain information from other postal operators and some NRAs cannot or do not collect data from operators other than the universal service provider.
Collection of market data is not uniform and it is not necessarily considered an aim of regulation or a key duty by NRAs in all Member States. Member States have interpreted Article 22a (1)(b) in different ways. In practice, although all Member States collect some statistics from their USPs there is a strong focus on services within the scope of the USO. Data on the parcel and express segment of the postal market is far less comprehensive and reliable than information on the letter market because most NRAs have until now not systematically collected data on domestic and cross-border parcel and express services outside the universal service obligation. While there is already a general collection of information on basic parcel delivery offers in most Member States, based on Article 22a of the Directive, this does not currently provide a broad picture of the full postal market. Some regulators have confirmed that they do not or cannot comprehensively collect data on parcels, whether for legal or resourcing reasons. Historically NRAs have focussed on the letter market (that was dominated by universal service providers) rather than the parcel market which has a larger number of operators and has been assumed to be more competitive.
The ERGP, in its reports on the cross-border parcel delivery market concluded that there was no need for a full market analysis or a collection of information based on full formal definition of the market and found no indication of a competition problem that it believed could best be dealt with by ex-ante regulation. The ERGP did however observe that comprehensive information to understand the functioning of the parcel market and possible competition problems in it could be useful. Differences between NRAs in the level of monitoring and type of data collected on the parcel market have also been noted.
Given the increasing importance of e-commerce related parcels for all postal operators and the need to ensure a single market in cross border parcel delivery, an improved and targeted data collection is imperatively needed to show developments in the market and help ensure effective competition.
2.10.Value Added Tax (VAT)
According to the VAT Directive Member States shall exempt the supply of public postal services from VAT. In 2003 the European Commission adopted a proposal to amend the (former) Sixth VAT Directive, with the objective to tax postal services and sales of postage stamps. This proposal was driven by the Commission’s concern that the VAT exemption for public postal services might create distortions on the postal market. After several years of negotiations in Council, no consensus was reached on this proposal and the Council agreed in December 2010 that the only realistic way forward was to keep the ‘status quo’. As a consequence, the Commission withdrew this proposal. Furthermore, the CJEU has – in the meantime - clarified the scope of the VAT exemption for public postal services. Nevertheless, the situation remains unsatisfactory in relation to the VAT treatment of the postal sector.
The exemption, as interpreted by the CJEU, generally covers postal services supplied by universal service providers in their capacity as such. Following full market opening in particular, the exemption creates a distortion because non–universal service providers (USPs) are obliged to charge their customers VAT (unlike the USP), which increases prices for consumers who are unable to claim back VAT, thereby reducing the attractiveness of using providers who do not qualify as a USP. On the other hand, since the USP is not able to claim back VAT yet must pay VAT on its inputs, there is some 'hidden VAT' which is passed on to consumers in the USPs' prices – and which cannot be claimed back by those who are eligible to do so. The VAT exemption could therefore be characterised both a benefit and a burden.
Member States also implement the exemption in different ways, potentially compounding the distortions already created through national variations in the scope of the USO. In responses to the 2012 consultation on parcel delivery, the VAT exemption was cited as one of the main barriers to a level playing field for e-commerce and parcel delivery by competitors of the universal service providers.
Figure 7: Scope of VAT Exempt Postal Services as a Percentage of EU/EEA Market
Source: WIK-Consult, Main Developments in the Postal Sector (2010-2013)
Since 2008 there has been a trend towards a reduction in the scope of the VAT exemption as a number of Member States have reduced the respective universal service scope. For example in Austria the VAT exemption was lifted from non-universal service products, that were understood to be all products not posted in a post office or a collection box. In Germany and the UK bulk mail is no longer VAT exempt, as are money orders in Bulgaria and industrial direct marketing mail in France. However, despite these changes the differences between Member States continue.
Other developments:
In February 2013, an appellate court excluded Deutsche Post from consideration in a tender procedure involving delivery of court documents due to its failure to include VAT in its bid. This followed Deutsche Post's lack of compliance with a 2010 decision that required VAT to be charged for the delivery of court documents.
In December 2012 the European Regulators Group for Postal Services published and consulted on a Report on the VAT exemption for postal services. The report found that the situation differs between Member States, including exempted services, exempted operators and the tax rate for non-exempted postal services. The VAT exemption was judged to affect competition, prices, welfare, make-or-buy decisions of operators, and the relative cost of postal services and competitive options open to different segments of customers.
In the context of the review of the VAT rules for the public sector which is currently being carried out, in January 2013 the Commission Directorate-General for Taxation and Customs Union published a study on VAT in the public sector and exemptions in the public interest, including postal services. The study found that the VAT exemption did create distortions, notably reducing the incentive to outsource and affecting the competitiveness of public and private entities. A subsequent public consultation (finalised in 2014) received some responses from the postal sector.
In April 2013 the Italian Competition Authority found Poste Italiane had failed to charge VAT on services which were no longer part of the USO including bulk mail, registered mail certified mail and direct mail. Poste Italiane was instructed to include VAT in all individually negotiated tariffs, following the aforementioned ruling of the CJEU ruling that individually negotiated tariffs should not be VAT exempt.
There is a long standing series of court cases brought by TNT Post UK (now Whistl) who challenge Royal Mail's VAT exemption (as the UK USP). The High Court in the UK ruled in October 2014 that the UK Government was right to exempt Royal Mail's mandated access services from VAT, though the Judge has said the case could ultimately be referred to the CJEU for a ruling, suggesting there were sufficient implications on postal market liberalisation in other EU Member States.
On 21 April 2015 the ECJ stated in Case C-114/14 "[...] that, by failing to exempt from value added tax the supply by the public postal services of services other than passenger transport and telecommunications services, and the supply of goods incidental thereto, and the supply at face value of postage stamps valid for use for postal services within national territory, the Kingdom of Sweden has failed to fulfil its obligations under Articles 132(1)(a) and 135(1)(h) of Council Directive 2006/112/EC of 28 November 2006 on the common system of value added tax.
2.11.Application of Competition Rules
The prevention of anti-competitive behaviour and the effective application of competition law are critical if consumers are to benefit from full market opening in the postal sector. This section summarises the main anti-trust cases, as well as rulings on mergers and acquisitions and State aid cases related to the postal sector, both at EU and national level.
In several Member States, national authorities (national competition authorities (NCAs) or national regulatory authorities (NRAs), where the latter have competition powers), have ruled that the universal service provider has abused its dominant position. Most cases alleged that the universal service provider had offered selective and discriminatory rebates in order to drive competitors out of the market, or to erect high barriers to entry. The other main type of case dealt with situations where operators had 'refused to deal', i.e. refused to grant access to non-replicable parts of the network. Cases therefore tended to relate to 'access' issues, following from Articles 11, 11a or 12. Many decisions were appealed in national courts. The Commission did not adopt any decision on the abuse of dominant position but fined one cartel in the freight forwarding sector which involved postal (express) operators.
Summary of cases:
In six Member States (DK, ES, IT, RO, SE, UK) NCAs took the view that rebates (or an equivalent failure to charge VAT) offered by the designated universal service provider hindered or excluded competitors. In 2012, in Post Danmark v Konkurrencerådet, the CJEU clarified the application of the competition rules to rebates by ruling that for price discrimination to breach competition rules it is necessary to show that ‘that pricing policy, without objective justification, produces an actual or likely exclusionary effect, to the detriment of competition and, thereby, of consumers’ interests’. Prices below average total costs in themselves are not sufficient.
In Ireland the Competition Authority concluded that between March 2012 and February 2013 the way in which An Post implemented its pricing scheme for publishers had the same effect as granting an exclusivity discount and was likely to a breach of Section 5 of the (Irish) Competition Act 2002 and/or Article 102 of the Treaty of the functioning of the European Union.
In two Member States (Spain in April 2013 and Luxembourg in December 2012), NCAs condemned public postal operators for ‘refusal to deal’, i.e. a refusal to provide certain services to particular customers without objective justification.
In France, in 2011, the Autorité de la concurrence, the NCA, rejected an agreement between public postal operators and networks of retail outlets. Although the agreement was non-exclusive, the NCA concluded that the agreement would substantially lessen competition.
In 2012, the Commission found that an agreement between freight forwarders, including Deutsche Post, involving shipments between the EU and China amounted to an anticompetitive price-fixing agreement. The agreement established the prices that all parties would charge customers for services such as document preparation, currency conversion, and peak season surcharges.
In the reporting period, three significant merger cases in the postal sector were the subject of decisions by the Commission.
In May 2009 the Commission approved, subject to conditions and obligations, the merger between Posten (Sweden) and Post Danmark. The decision was conditional on the commitment of the parties to divest assesses and customer contracts covering their entire overlap in the domestic standard business to business (B2B) parcel delivery services market in Denmark.
In July 2012, the Commission cleared, subject to conditions, the creation of Asendia, a joint venture between the French La Poste and Swiss Post to provide international mail services in various Member States.
In January 2013, the Commission prohibited the proposed acquisition of TNT Express by UPS because it found the merger would reduce the number of major competitors from three to two and would significantly impede effective competition in 15 national markets.
In April 2015 FedEx Corporation and TNT Express N.V. announced they had reached conditional agreement on a merger. The Commission subsequently announced the proposal would be subject to a merger approval investigation by the Commission.
Article 7 of the Postal Service Directive permits the financing of the net cost of the universal service through general taxation. A number of public postal operators have been recipients of state aid, often justified by cost of providing postal networks in remote and rural regions. Several operators have received aid for restructuring purposes. While such aid may be permissible, a level playing field between universal service providers (who were frequently heavily subsidised in the past) and competitors is an important requirement for the success of market opening – and lower prices for consumers. By setting out approaches that are consistent with Annex 1 to the Postal Services Directive, the Annex on the Calculation of the Net Cost of the Postal Universal Service Obligation aims to create greater certainty over methodologies for the net cost calculation.
State aid decisions 2009-2015:
Seven Member States (Belgium, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Poland and the UK) had compensation approved for compensation for providing services such as maintaining the postal network in unprofitable areas and providing low tariffs for certain types of mail (e.g. press or election material) or for certain customers (e.g. the blind and partially sighted). The Commission found aid justifiable in all cases except Belgium where it concluded that overcompensation was paid to bpost (though some aid was also justified).
Three cases concerned compensation for the high costs of previous public sector pension systems (Belgium, Germany and the UK). Such aid is considered justifiable if the result is that the public postal operator still has to finance from its own revenues an amount of social security contributions that are equivalent to those of private competitors. In one case the Commission ordered the State to recover part of the aid as the beneficiary (Deutsche Post) was finally paying less than competitors in terms of social security contributions.
Two cases (Greece and UK) dealt with aid for corporate restructuring and modernisation. These were considered compatible with EU competition rules.
One case involved the French government’s guarantee of the debts of the public postal operator. The Commission concluded that debt guarantees gave La Poste an economic advantage over its competitors. France lost its appeal of this decision and the CJEU upheld the General Court's judgement that confirmed the Commission’s finding that La Poste's status as an EPIC (Établissement Public à caractère Industriel et Commercial) resulted in an advantage to the undertaking in the form of an implicit unlimited guarantee.
3.Market Developments in the Postal Sector
3.1.Sector Overview
Between 2007 and 2011 the overall value of the EU postal sector decreased slightly from EUR 94 billion to EUR 91 billion (accounting for 0.72% of EU28 GDP). While the revenues in the parcel and express sector have grown, demand and revenues for letter post services have declined. Changes in the overall structure of the postal sector have continued and accelerated: parcel and express revenues accounted for more than half the total revenues generated in the sector in 2011, compared to 44% in 2007. This proportion is likely to have increased given the ongoing decline in letter volumes and growth in the parcel market.
In 2013 the universal service area alone (i.e. products and services falling within the scope of the universal service) accounted for more than EUR 23 billion for the EU28. Over 85 billion letter post items were dispatched in the EU by universal service providers in 2013, as were nearly 2 billion parcels.
3.1.1.Ownership Structures of Universal Service Providers
The Directive does not require any particular ownership structure for the postal operators providing the universal service. Nevertheless, in all Member States except Cyprus the USP is organised as a corporation under normal corporate law or related governance arrangements for state-owned enterprises. Cyprus Post is a ministerial (government) department.
The majority of universal service providers remain publicly owned at least in part: Post NL, Malta Post and CTT Correios (Portugal) are the only wholly privately owned operators. The proportion of government ownership has however diminished since 2008 with several governments selling a partial stake or more in their national operator. Greece announced plans to sell a 39% stake in Hellenic Post in 2010.
Royal Mail (UK) was privatised in October 2013. 60% was sold to institutional and retail investors and 10% was allocated to eligible employees for free. The UK government announced in June 2015 that it would sell its remaining shares and sold half its remaining stake later that month.
CTT Correios was fully privatised in September 2014 when the Portuguese Government sold its final 31.5% stake.
The Romanian state decided in 2012 to begin the privatisation of Romanian post. A non-binding offer, submitted by bpost, was accepted for the acquisition of a 51% stake in February 2015. This agreement enabled due diligence to start, prior to the submission of any binding offer.
Italy envisages the privatisation of Poste Italiane in 2015. An application for listing on the Milan Stock Exchange was made in August 2015.
3.1.2.Financial Position of Postal Operators
Figure 8: Profitability of USPs (EBIT margin, total business)

Source: WIK-Consult, Main Developments in the Postal Sector (2010-2013), p201
It is difficult to discern trends in the profitability of universal service providers: some have become more profitable others less so. Other postal operators do not always publish their financial results, and where they do they are often not on a comparable basis to those of the universal service providers so comparisons different types of operator can be difficult. Market developments, for example the experiences of Bring Citymail and many German competitors; the market exits of Adrexxo from the French letter post market; and TNT Post's withdrawal from some Eastern and the Austrian letter post markets and suspension of end to end delivery in the UK, have been interpreted as an indication that new entrants may be less profitable than some universal service operators, though there could also be other factors at play.
The decline in letter post volumes affects the economic situation of postal operators, particularly universal service providers which have diversified less into other sectors such as financial services. The immediate effect of declining volumes is shrinking revenue, particularly in the short term before business practices and/or prices can adapt and affected by the high share of fixed costs that are typical of postal operators with high frequency national networks. One model of the financial impact on postal operators of the decline in letter volumes suggests that smaller providers who have lower mail volumes are likely to face a higher impact on their costs for a given percentage decline in volumes as the fixed element of the costs are concentrated on a smaller number of items.
3.2.Letter Post Markets
The key players in the letter post sector are still the universal service providers. In most Member States they retain market shares above 95% in terms of volume and revenues. Nevertheless, in some domestic letter post markets delivery competition with market shares above 5% has emerged, notably in Estonia, Croatia, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Denmark, Poland, Spain and Sweden.
3.2.1.Letter Volumes and Revenues
Two major dynamics have fundamentally altered the letter post markets since 2008: the economy and e-substitution. The first has often reinforced the latter as governments, businesses and individuals have sought to save costs and therefore switched to electronic means of communication and the provision of information and services, which have also become increasingly convenient for individuals (and businesses) to access as technology has developed.
Economic activity was historically the main driver of letter volumes. Countries with higher levels of GDP had higher quantities of mail per capita. Although economic activity does still affect mail demand to some extent, the rate of e-substitution is also now a key determinant of letter volumes. Factors affecting e-substitution include price, internet availability and penetration, user habits, reliability of services and security concerns. Communication between individuals has already been replaced by electronic communication to a significant extent, whereas concerns about the security of electronic communication may be responsible for the slower rate of e-substitution in communications between businesses and consumers.
In 2011 the EU letter post sector accounted for a total of EUR 44 billion or 0.34% of EU27 GDP. This compared to EUR 52.3 billion in 2007.
Figure 9: Estimated Number of Letter Post Items 2008 to 2013
Source: UPU estimate for EU27. Shows letter post items dispatched by designated operators (i.e. universal service providers) only.
Figure 10: Domestic letter post items per capita (2007 and 2011)

Source: WIK-Consult, Main Developments in the Postal Sector (2010-2013), p167
Figure 11: Total letter post items per capita (2012 and 2013)
Source: European Commission Postal Statistics Database
The Western Member States still have on average the highest letter post volume per capita with 217 items per capita in 2013. Residents of the Southern and Eastern Member States received only 72 letter post items and 53 letter post items respectively per year on average. In the European Union (EU28) in 2013 the average was about 141 items per capita.
In 2011, the largest letter post markets in terms of absolute revenue and volume were Germany, the UK and France followed by Italy and Spain in terms of revenue share and Spain and the Netherlands respectively in terms of volume share.
In 2013 the largest letter post markets in terms of volume were Germany, France and the UK.
Figure 12: Average change rate per year for domestic and cross-border inbound letter post volumes 2007-2011
Source: WIK-Consult, Main Developments in the Postal Sector (2010-2013), p169.
Between 2007 and 2010 letter volumes declined on average by 4.3% per year and letter revenues by 5.2% per year. Between 2010 and 2011 the letter decline slowed to 3.3% in terms of volumes and 1.4% for revenues.
Figure 13: Changes in total letter mail 2012 -2013
Source: European Commission Postal Statistics Database
Between 2012 and 2013 the decline of letter volume is estimated to be 4.85% for EU28. On the basis of the latest information, there are indications suggesting that the decline of letter mail revenues may have bottomed-out. However, it is still early to draw firm conclusions at this stage, not least as volumes continue to decline.
The decline in the volume of letters is not uniform across the EU. Between 2007 and 2011 the average decline in western Member States was 3.9%. Denmark experienced an average annual decline of over 10% and the UK average reductions of over 6%, whereas Austria, Finland and Luxembourg saw declines of less than 2%. Although they started from a lower baseline, in percentage terms both southern Member States and eastern Member States saw higher rates of decline, with an average of 6% and 8% respectively. Bulgaria, Estonia, Lithuania and Latvia all saw letter volumes fall by over 8% (and Romania was just under 8%).
The picture between 2012 and 2013 is slightly different. Mail decline is smoother in most of the Member States and some Member States experienced marginal growth. On the other hand, Cyprus, Greece and Spain experienced a significant decline, potentially as a result of economic circumstances.
Nevertheless, some Member States continue to experience steep declines in the number of letters. For example in the Netherlands addressed mail volumes declined by around 8%in 2014 and by 13% for the first quarter of 2015. Mail volumes in the Netherlands are less than half than they were in 2000, and overall volumes are predicted to fall between 32% and 49% between 2010 and 2020. In Finland addressed mail fell by 10% between January and September 2014 and the number of letters, bulk mail and magazines is estimated to fall from 1400 million in 2010 to 1000 million in 2015 to 350 million in 2013.
Figure 14: Decline in Addressed Letter Volumes 2000 - 2014 for Selected Member States
Source: Posti analysis
Two of the Member States with highest rates of decline in letter volumes, Denmark and Estonia are two of the most digitally advanced. Since January 2012 almost 90% of Estonian inhabitants have had an ID card that links them to online services and acts as a ticket for public transport. Electronic voting in elections has been an option since 2005, with 24% using this method in 2011. Over 90% of income tax declarations are now done online, as are 98% of banking transactions.
According to 2013 projections, by the end of 2014 the volume of stamped standard mail sent within Estonia was expected to fall by 43% compared to the year 2011
and during 2014 turnover from the domestic letter service fell by 8%.
Digital services are becoming mandatory for interactions between the Danish Government and citizens in four stages finishing in 2015. Municipalities and regional authorities, as well as many utility companies and financial services organisations communicate with citizens/customers via "e-boks"an electronic communications system jointly owned by Post Danmark and Nets A/S, a Danish payment systems provider. Mail volumes declined by 12% in 2014 and by 15% in Q1 2015 in Denmark.
3.2.2.Competition in Letter Post Markets
Overall, despite the gradual process of full market opening across the EU, the level of competition for letters remains limited in most Member States, in both domestic and international markets.
Of the Member States that fully opened their markets before 2011, eight Member States had over 5% competition by 2013. Bulgaria, Estonia, the Netherlands and Sweden had more than 5% end to end competition; Slovenia and the UK had more than 5% access competition; Germany had over 5% by volume of end-to-end and access competition; and Spain had over 5% competition (of an unspecified type). Several Member States who opened their markets later were known to have competition in over 5% of the letters market by mid-2013, including Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Romania and Slovakia.
Explanations for the slow development of competition will vary between Member States. Reasons include combinations of declining letter volumes, access regimes and special tariffs, other regulatory features and the cost of setting up a distribution network or the existence of other operators in adjacent markets (for example newspaper delivery). An ERGP report, on a preliminary evaluation, found that the level of end-to-end competition did not appear to have been influenced by letter volumes, population density or urbanisation. The level of urbanisation did not appear to have an impact on the development of access competition.
Table 6: Level of End to End and Access Competition in 2013
|
Member State
|
Year of full market opening
|
More than 5% end-to-end competition by volume
|
More than 5% access competition by volume
|
|
Austria
|
2011
|
No
|
No
|
|
Belgium
|
2011
|
No
|
No
|
|
Bulgaria
|
2011
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Cyprus
|
2013
|
No
|
No
|
|
Czech Republic
|
2013
|
No
|
No
|
|
Denmark
|
2011
|
No
|
No
|
|
Estonia
|
Before 2008
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Finland
|
Before 2008
|
No
|
No
|
|
France
|
2011
|
No
|
No
|
|
Germany
|
Before 2008
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
Greece
|
2013
|
No
|
No
|
|
Hungary
|
2013
|
No
|
No
|
|
Ireland
|
2011
|
No
|
No
|
|
Italy
|
2011
|
No
|
No
|
|
Latvia
|
2013
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Lithuania
|
2013
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Malta
|
2013
|
No
|
No
|
|
Netherlands
|
2009
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Poland
|
2013
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Portugal
|
2012
|
No
|
No
|
|
Romania
|
2013
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Slovakia
|
2012
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Slovenia
|
2011
|
No
|
Yes
|
|
Spain
|
2011
|
Unknown*
|
Unknown
|
|
Sweden
|
Before 2008
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
United Kingdom
|
Before 2008
|
No
|
Yes
|
Source: ERGP, (13) 38 rev1 Report on End-to-End Competition and Access in European Postal Markets. *Spain has more than 5% competition but was unable to define whether this was end to end or access competition.
Examples of competition in the letter market include the following:
Netherlands: two main competitors Sandd, a privately owned mail company and Selekt Mail (owned by Deutsche Post Global Mail) slowly gained market share from 2002. Selekt Mail was taken over by Sandd in 2012 and combined they had a market share of between 10 and 20% in 2012. PostNL (formerly TNT Post) also offers low budget mail services via its subsidiary Netwerk VSP. Competition is primarily for direct mail and periodicals.
Germany: The CITIPOST Verbund, founded in 2009, consists of 28 local postal operators and delivers to around 5.5 million households in Germany in both rural and urban areas. The cooperation partners deliver on average half a million items per day, five days a week, via 12,000 delivery routes. In 2012 they delivered around 125 million letter post items in total.
Poland: By 2013, InPost was delivering letters and parcels to about 75% of households in Poland and was forecast to deliver up to 230 million letters and up to 5 million parcels. By the end of 2014 Interger,pl SA Group (the parent company) had 8,300 customer service centres in Poland.
Spain: Competitors in Spain have a high market share of more than 18% (volume-based), with Unipost the largest alternative postal provider covering 70% of the population. Unipost specialises in the delivery of direct mail up to 500g but also delivers correspondence, registered mail, small packets and parcels received from its international stakeholder DHL.
Croatia: City Ex, owned by the private equity company Bancroft PE since 2011, delivered more than 60 million documents per year. However, it recently announced that it will withdraw from the letter mail market, lay off around 700 employees and focus on parcel delivery services. Austrian Post also operates in Croatia.
3.2.3.Cross-border Letter Post
While in many Member States there is limited or no competition in the cross-border letter post market, in other cases, usually western or southern Member States, there was more competition in the international than the domestic letter market. Where there is competition it is usually concentrated in the business or bulk mail markets where mail can be collected directly from customers rather than from a network of collection points.
Where there are competing operators for cross-border letter post, they tend to be universal service providers or their subsidiaries from other Member States, such as Spring Global Mail (a joint venture of Royal Mail and TNT), Asendia (joint venture of La Poste and Swiss Post) and Deutsche Post Global Mail. IMX, based in France, is the only independent operator with a significant market share. These operators are active mainly in western and southern Member States. The intensity of competition differs between locations.
3.2.4.Outlook
Studies predicting future changes in mail volumes anticipate that transactional/bulk mail will be the most affected between 2010-2020, with estimates ranging from a fall of 1.9% to 9.5% in the compound annual growth rate (CAGR). Social mail, 'office mail' and government communications are all expected to decline, as is marketing/advertising mail, though to lesser extents.
Table 7: Forecast change in volumes per letter market segment
|
|
Segment
|
Forecast period
|
CAGR min
|
CAGR max
|
|
Copenhagen Institute for Futures Studies (Europe)
|
Transactional mail
|
2010-2020
|
-3 %
|
-4 %
|
|
|
Gov2C
|
|
-2.5 %
|
-3 %
|
|
|
Marketing communication
|
|
-1.1 %
|
-1.7 %
|
|
|
Media content
|
|
-1.8 %
|
-2.7 %
|
|
|
Social communication
|
|
-2.3%
|
|
|
WIK-Consult (NL)
|
Social mail
|
2010-2020
|
-2.7 %
|
-5.3 %
|
|
|
Office mail
|
|
-2.6 %
|
-6.2 %
|
|
|
Transaction mail
|
|
-5.3 %
|
-9.5 %
|
|
|
Advertising
|
|
-1.6 %
|
-4.3 %
|
|
|
Periodicals
|
|
-2.1 %
|
-4.5 %
|
|
|
International mail
|
|
-1.5 % (inbound),
-1.5 % (outbound)
|
-3,9 % (inbound),
-4,1 % (outbound)
|
|
Koppe/Hömstreit (AT)
|
Transaction mail
|
2009-2025
|
-1.9 %
|
-5.7 %
|
Source: WIK-Consult, Main Developments in the Postal Sector (2010-2013), p180.
Figure 15: Trend forecast for total universal service mail volumes in the Netherlands 2010-2020

Source: WIK-Consult, Developments in the Dutch Postal Market, 2011
3.3.Parcel and Express Markets
3.3.1.Parcel and Express Markets Overview
The parcel and express market is more heterogeneous than the letter market and more complex. There are five main types of operator. The parcel, express and courier market did not form part of the reserved area for universal service providers prior to market opening.
Universal service providers are required by the Postal Services Directive to arrange for the clearance, sorting, transport and distribution of postal packages up to 10kg, and potentially up to 20kg. This obligation includes domestic and international parcel services. In addition to the basic parcel services, which fall within the scope of the Postal Services Directive, universal service providers usually also offer a range of value-added services, for example track and trace and guaranteed delivery times. Such services compete with those offered by integrators and other domestic and international carriers.
Providers of postal services other than the universal service provider are covered by the Postal Services Directive notably:
Article 9 permits services falling outside the scope of the universal service to be covered by a general authorisation condition. This may include requirements concerning the quality, availability and performance of the relevant services, if necessary and justified; be subject to an obligation to make a financial contribution to the national regulatory authority's operational costs referred to in Article 22; be made subject to or impose an obligation to respect working conditions; and be subject to an obligation to make a financial contribution to the sharing mechanism (to the extent that services offered are within the universal service area).
Article 19 requires that all postal service providers have transparent, simple and inexpensive procedures for dealing with postal users' complaints.
Article 22a requires all postal service providers to prove all the information, in particular to national regulatory authorities, to ensure conformity with the directive and for clearly defined statistical purposes. The information requested by NRAs should be proportionate to its tasks.
"Integrator" is the term used to refer to the four main international express carriers, DHL (part of Deutsche Post DHL group), Fed EX, TNT and UPS who combined account for 87% of the international express market. Copenhagen Economics estimated that the integrators had a 42% market share in e-commerce deliveries (compared to 40% for universal service providers), rising to a 50% share for cross-border e-commerce shipments. The four companies operate on a global scale and have either full ownership or operational control of their networks, including transport assets such as aircraft and IT. These companies offer 'express' services with guaranteed delivery times and tracking both within and between countries. Traditionally much of their business was in the B2B segment, though they are now expanding into B2C markets following the emergence of e-commerce. In the B2B segment, the four integrators have a combined market share in the intra-European cross-border express segment of approximately 90%. The largest market player in the European international; express market is DHL with an estimated market share of 41%, followed by UPS with an estimated market share of 25%, TNT with estimated 12%. FedEx is the smallest player with approximately 10% market share. FexEx and TNT announced a proposed merger in April 2015 after the European Commission ruled against the proposed takeover of TNT by UPS in 2014.
Pan European parcel networks created by national operators, including DPD, the international parcel delivery network of Le Groupe La Poste and Global Logistics Systems (GLS) a European delivery company and subsidiary of Royal Mail. Both companies have a road-based pan European parcel network.
Other national operators / universal service providers also have some degree of parcel capability to fulfil the requirements of the universal service obligation. They therefore have to provide basic domestic and cross-border parcel services, though in many cases the latter end at the border where the parcel in question is handed over to the national operator of the recipient country. Some national operators also have regional networks that provide domestic and cross-border services, though not on the same scale as the integrators or DPD or GLS. Examples include Austrian Post's European Distribution Network EURODIS, Eesti Post/Omniva, Post Nord and Post NL. Around 36% of the parcel market is held by universal services providers, and only around 10% of the parcel market falls under the universal service obligation. Reflecting their wider (i.e. non USO) parcel offering, USPs have been estimated to have a 35% market share for the delivery of B2C packets and parcels, growing to 54% in the more mature e-commerce markets. Their share of the domestic parcel and express market has been estimated at 20%.
Many privately owned small and medium sized courier companies provide courier, express and parcel (CEP) services. These are usually on a B2B basis such as Nightline (IE), Siodemka (PL) and MRW (ES and PT). Crowdsourcing is also starting to appear as a possibility for parcel delivery through services such as bring.BUDDY (in conjunction with DHL).
Finally, the increase in e-commerce has led to a growth in new parcel delivery companies, or the development of those created for catalogue shopping. Examples include Hermes (DE) and Yodel (UK). Competitors in letter markets such as Sandd (NL), InPost (PL) and City Ex (HR) have also begun to enter the parcel market.
The main players in the European CEP market are shown below.
Figure 16: European CEP Market for the Express and Deferred Segments in Revenue
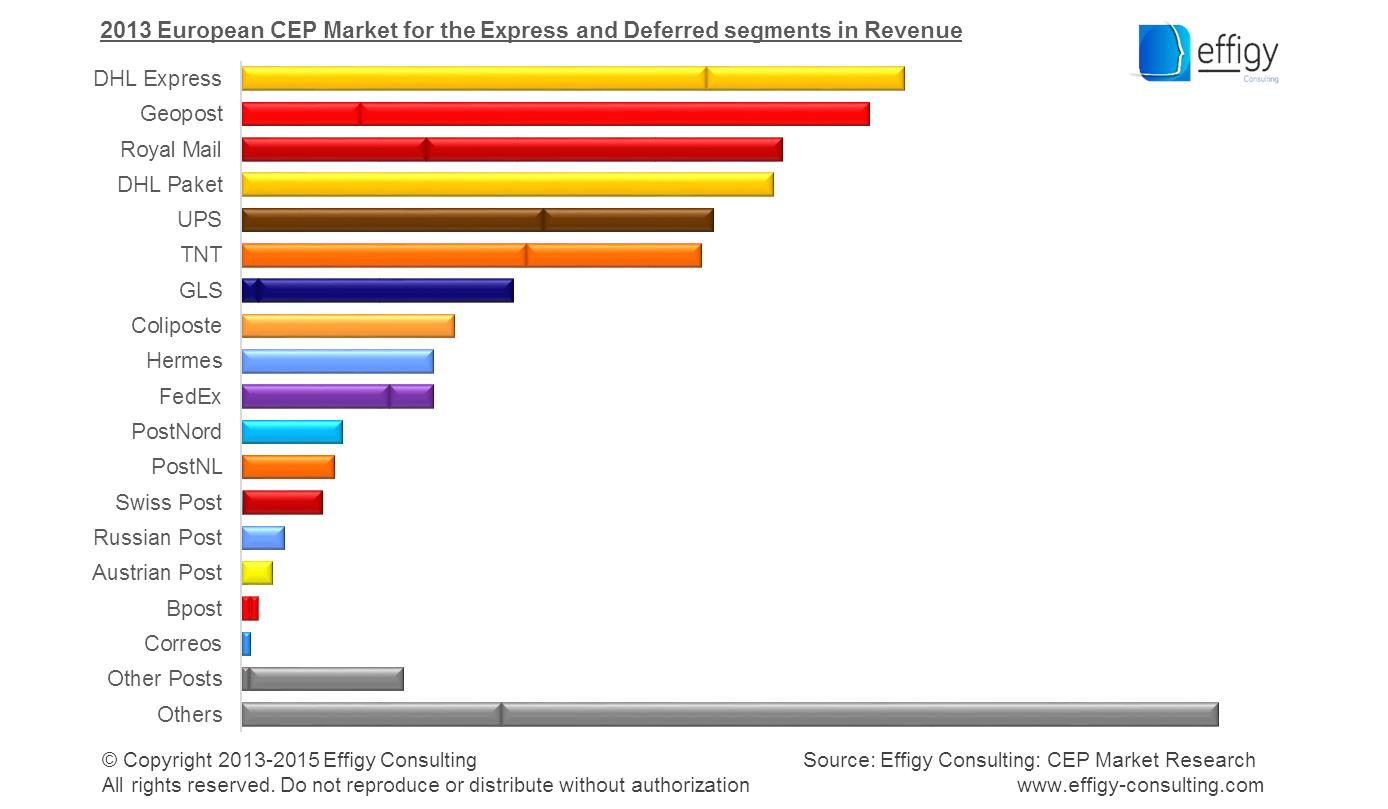
Source: Effigy Consulting European CEP Market Research.
There is no up to date comprehensive information or consensus about the size of the European parcel and express market. This is mainly due to different market definitions, especially regarding the weight limit of shipments and the service characteristics, different methodologies as well as a lack of data. Many smaller packages, usually weighing less than 2kg and which fit a ‘large letter’ format, including books, CDs and DVDs are classified as 'packets' and therefore posted as 'letters' rather than parcels. This may to result in the understatement of e-commerce growth since such packets are particularly convenient for e-commerce as they will often fit through a letter box rather than requiring specific collection arrangements.
Estimates of the size of the parcel market include:
TNT Express estimated that the European parcel and express market had a value of EUR 60 billion in 2010. The European Express Association estimated the European express market was worth EUR 38 billion in 2010.
A 2011 A.T. Kearney study estimated the parcel market to be worth around EUR 47 billion.
A 2013 WIK study estimated a market size of EUR 37 billion for the European parcel and express market in 2011.
Copenhagen Economics valued the European courier, express and parcel market at EUR 46 billion in 2011.
La Poste estimated the intra-European parcel and express market generated EUR 37 billion in 2011 and valued the courier, express and parcel market was worth EUR42.8 billion in 2012.
DHL Deutsche Post, estimated a market size of EUR 6.8 billion for the European express market in 2011.
Apex estimated the European parcel market to be worth EUR 53.5 billion in 2014.
Figure 17: Parcel and Express Market Segments (2011)

Source: WIK-Consult, Main Developments in the Postal Sector (2010-2013), p225
Figure 15 illustrates the heterogeneous structure of national parcel and express markets within Europe. Overall, express services only account for one quarter of domestic but more than half of the cross-border market segments. It appears that in Member States with relatively ‘slow’ standard parcel services (i.e. delivery times of two or more working days), e.g. in Spain, Italy and France, domestic express services have a greater market share than in Member States with high-quality standard services (i.e. next day delivery of standard parcels) e.g. in Germany and the UK.
3.3.2.Parcel Volumes and Revenues
In contrast to the letter post sector, the EU parcel and express sector is growing rapidly. Parcel volumes increased to around 6.4 billion items in 2011 (up from 4.8 billion items in 2008, i.e. by 33%). Parcel volumes per capita were highest in the Western Member States with 20 parcels per person per year on average, though in reality only Germany and the UK exceeded this average with over 25 parcels per capita each in 2011. This is not surprising because distance selling and e-commerce are well established in these Member States. In Southern and the Eastern Member States there were five and two parcels per person (respectively) in 2011, and in the European Union (EU27) the average was 13 parcel items per capita.
The proportion of domestic express and parcel services has been estimated to be roughly 70% of total revenues and 90% of total volumes. 10% of cross-border and 43% of domestic volumes were estimated to have come from B2C shipments in 2010.
Figure 18: Parcel Market Size (EUR billion) and Growth (CAGR) by Country
46.346.344.844.8CAGR 2009-2014CAGR 2009-2014Revenue EUR billionRevenue EUR billion
Source: Apex, European Parcels: Market Insight Report 2015. Key shows CAGR 2009-2014. Figures inside each column show revenue in EUR billion for that Member State (according to the key). Figures above each column show European parcels market size in EUR billion.
Estimates of the market structure and relative sizes also differ, though both A.T. Kearny and WIK-Consult estimate that the three biggest markets (Germany, France and the UK) account for more than half of the European parcel and express sector.
Figure 19: Estimated Number of Ordinary Parcels Dispatched by Universal Service Providers 2008-2013
Source: UPU estimate for EU27. Shows ordinary parcels dispatched by UPU designated operators (i.e. universal service providers) only.
Figure 20: Parcels per capita (2011)

Source: WIK-Consult, Main Developments in the Postal Sector (2010-2013), p225
Figure 21: Domestic ordinary parcels per capita delivered by USPs (2012 and 2013)
Source: European Commission Postal Statistics Database
Western Member States have on average a higher per capita distribution compared to the eastern and southern Member States. As did letter volumes, parcel, and particularly express, volumes and revenues dropped substantially in the aftermath of the 2007/08 financial crisis. European courier, express and parcel revenues fell by 9% between 2008 and 2009 and volumes declined by 2% as businesses sought to negotiate cheaper contracts, switched from express to less expensive services and the proportion of lighter B2C shipments increased. Cross-border shipments were more affected than domestic ones. However by 2010 volumes had recovered to their 2008 levels, though revenues continued to be lower than they previously were. In 2010 and 2011 the European CEP market grew by 6% in volume and 4% in revenue.
Per capita volumes for (ordinary) parcels
between 2012 and 2013 also suggest that there is an observable overall increasing trend, though growth was clearly much stronger in some Member States than others.
Christmas 2014 generated record volumes for European postal and parcel operators. For example in Finland Posti delivered 9% more packages in December than in 2013, e-retail over the Christmas period in the UK grew by 13% (compared to 2013) and in the UK online retail is expected to continue double digit growth at 12% in 2015. On one day in December 2014 Austria Post delivered a record 470,000 parcels, 40,000 more than in 2013 and almost double the usual daily volume. Post Nord also posted a new volume record, delivering around 455,000 parcels in one day, almost 30,000 more than the previous record in 2012.
3.3.3.Competition in Parcel Markets
Although the parcel market is usually thought to be more competitive than the letter post, in many Member States it is dominated by the larger operators who in many cases have a combined market share of over 60%.
The international cross-border parcel and express market accounts for approximately 30% of the revenues and 9% of the volume of the parcel and express market. This segment is highly concentrated with an average market share of the biggest operators of approximately 75 to 95% depending on the Member State under consideration. Cross-border parcel and express services are dominated by B2B shipments.
Table 8: Market Share of Universal Service Providers in Domestic Parcel and Express Markets (2011)
|
<10% market share
|
10-20% market share
|
>20% market share
|
|
Bulgarian Post (BG)
Cyprus Post (CY)
ELTA (EL)
Correos (ES)
Polish Post (PL)
CNPR Compania Nationala Posta Româna (RO)
|
bpost (BE)
Croatian Post (HR)
An Post (IE)
Poste Italiane (IT)
Lithuanian Post (LT)
Latvijas Pasts (LV)
MaltaPost (MT)
|
Österreichische Post (AT)
Česká pošta (CZ)
Deutsche Post DHL (DE)
PostDanmark/PostNord (DK)
Eesti Post (EE)
Itella (FI)
La Poste (FR)
Magyar Posta (HU)
PostNL (NL)
CTT Correios (PT)
Posten/PostNord (SE)
Slovenian Post (SI)
Slovenska Posta (SK)
Royal Mail Group (UK)
|
Source: WIK-Consult, Main Developments in the Postal Sector (2010-2013), p239
Table 6 shows estimates of the market position of universal service providers in their respective domestic parcel and express markets. Most universal service providers have a market share above 20% in their domestic parcel and express market. However, their relatively strong position is mainly supported by their dominance in the B2C segment (parcel delivery) and less by their role in the B2B segment and, in particular, in the express segment where national postal operators usually play a minor role.
Table 9: Main alternative operators active in domestic and cross-border B2C delivery
|
|
Number of operators
|
Main operators active in domestic B2C delivery except USP and integrators
|
Number of operators
|
Main operators active in cross-border B2C delivery except USP and integrators
|
|
AT
|
4
|
DPD, GLS, Hermes, Asendia
|
3
|
DPD, GLS, Hermes
|
|
BE
|
5
|
DPD, GLS, PostNL, Kiala, Mondial Relay
|
6
|
PostNL, GLS, G3 Worldwide, Swiss Post, Hermes, DPD
|
|
BG
|
6
|
DPD, Econt Express OOD, Tip Top Courier AD, M&BM Express OOD, GLS
|
2
|
GLS, DPD
|
|
CY
|
1
|
ASC Courier
|
1
|
ASC Courier
|
|
CZ
|
2
|
DPD, GLS
|
2
|
GLS, DPD
|
|
DK
|
3
|
DPD, GLS, Bring
|
4
|
DPD, GLS, Bring, DB Schenker
|
|
EE
|
2
|
DPD, Itella
|
2
|
DPD, Itella
|
|
FI
|
3
|
DB Schenker, Matkahuolto Oy AB, Posten Åland
|
3
|
DPD, DB Schenker, GLS
|
|
FR
|
6
|
Colis Privé, Kiala, Mondial Relay, Relais Colis, Exapaq, Hermes
|
3
|
Kiala, Exapaq, Hermes
|
|
DE
|
5
|
DPD, GLS, GO! General Overnight Service, Hermes, Pin Mail AG
|
5
|
DPD, GLS, GO! General Overnight Service, Hermes
|
|
EL
|
5
|
ACS S.A., TACHYMETAFO-RES ELTA S.A., GENIKI TACHYDROMIKI, Speedex, ACS Courier
|
3
|
World Courier, Speed Air, ACS Courier
|
|
HU
|
3
|
DPD, SPRINTER Kft., GLS
|
4
|
DPD, GLS, SPRINTER Kft., GTR
|
|
IE
|
5
|
DPD, Nightline, GLS, Citypost, DB Schenker
|
5
|
DPD, Nightline, GLS, Citypost, DB Schenker
|
|
IT
|
3
|
GLS, Hermes, BRT Corriere Espresso
|
3
|
GLS, BRT Corriere Espresso, Hermes
|
|
LV
|
3
|
DPD, Itella, GreenCarrier
|
2
|
DPD, Itella
|
|
LT
|
2
|
DPD, Itella
|
2
|
DPD, Itella
|
|
LU
|
4
|
DPD, Kiala, Hermes, Mondial Relay
|
3
|
GLS, DPD, Hermes
|
|
MT
|
3
|
GLS, Arrow Express, Miles Express
|
1
|
GLS
|
|
NL
|
4
|
DPD, Kiala, GLS, Hermes
|
3
|
DPD, GLS, Hermes
|
|
PL
|
3
|
GLS, Siódemka, InPost, DPD
|
4
|
DPD, GLS, Siódemka, Hermes
|
|
PT
|
4
|
GLS, Nacex, Enviália, MRW, Torrestir
|
6
|
Enviália, MRW, Nacex, Chronopost International, Torrestir
|
|
RO
|
7
|
DPD, Cargus International, GLS, Fan Courier Express, Sprint Curier Expres, Urgent Curier
|
7
|
DPD, Cargus International, GLS, Fan Courier Express, Sprint Curier Expres, Urgent Curier S.R.L.
|
|
SK
|
3
|
DPD, GLS, ReMax
|
2
|
DPD, GLS
|
|
SI
|
3
|
DPD, GLS, Doortodoor
|
2
|
DPD, GLS, Doortodoor
|
|
ES
|
5
|
Kiala, GLS, Enviália, Tourline Express, Mondial Relay
|
4
|
GLS, Enviália, Chronopost International, Tourline Express
|
|
SE
|
3
|
DB Schenker, Bussgods, Bring
|
2
|
DB Schenker, Bring
|
|
UK
|
12
|
DPD, Hermes, HDNL/Yodel, City Link, UK Mail, Interlink, Nightfreight, APC, DX, City Sprint, XDP
|
9
|
DPD, HDNL/Yodel, City Link, UK Mail, Nightfreight, DX, City Sprint, XDP, Hermes (to Austria and Germany)
|
Source: Copenhagen Economics, E-commerce and delivery - Study on the state of play of EU parcel markets with particular emphasis on e-commerce, 2013, p118
E-commerce is however driving change. B2C delivery has specific requirements notably regarding cost-efficient organisation of the last mile (delivery to consumers) and the management of returns, notably the necessity to provide reliable C2B return channels as clothes and shoes become increasingly popular online purchases. Some examples of market developments include:
Web-based delivery: web-based delivery solutions which connect e-retailers to same day delivery companies (e.g. Shutl, now owned by ebay) or provide an e-retailer integration with a range of carrier networks (e.g. Metapack).
More frequent delivery options: from September 2014 Royal Mail started delivering parcels within the M25 area of London and opening around 100 enquiry offices on Sundays. GLS has also started evening and Saturday delivery services in selected cities in Germany.
Cross-border cooperation to enter new markets, for example Hermes and Austrian Post's cooperation with Hermes Logistik Gruppe.
Many postal operators are rolling out parcel lockers which enable customers to collect and return parcels from a bank of lockers at a convenient location, such as a train station. Lockers might be accessible 24/7 and the consumer will enter a code (valid for a set period of time) to gain access to the locker. Bpost for example have lockers at 125.
Postal operators are also making use of retail outlets where customers can collect their parcels, in addition to retailers offering 'click and collect' services whereby consumers buy online but collect their item from a (physical) retail outlet.
Parcel delivery drones have been trialled by La Poste, Amazon and other delivery operators. DHL have trialled a 'parcel copter'.
3.3.4.Cross-border Parcel Delivery
The 2012 Communication on e-commerce and online services identified the delivery of goods purchased online as one of the five main priorities to boost e-commerce. Following this, a Green Paper consultation An integrated parcel delivery market for the growth of e-commerce in the EU was published to seek further details of the problems in the market and possible solutions to address them. Cross-border delivery was considered to be an obstacle by 57% of retailers and almost half of consumers worried about the delivery element of cross border transactions. In the resulting discussion, a broad consensus seemed to emerge about the urgent need to address certain issues.
The 2013 Roadmap set out a series of actions to improve the availability, affordability and accessibility of cross-border parcel delivery services. Central to this was an industry initiative by universal service providers to improve the quality of service: because the parcel services provided by universal service providers have developed primarily for their domestic market, systems and operating practices were often incompatible. This resulted for example in the need to re-label items on arrival in a different Member State and a lack of cross-border track and trace services. The 'Interconnect' programme developed by universal service providers is comprised of five areas: flexible delivery options: easy and seamless return solutions: track and trace capability for lightweight products; improved customer services and harmonised labelling. These features are being rolled out on an operator-by-operator basis so they will be at introduced at different times in different Member States. The Commission is monitoring the extent to which these new products and services meet customer needs, following the expiry of the 18 month deadline in June 2015 envisaged by the Roadmap and will include an assessment of progress in the forthcoming Impact Assessment for the cross-border parcel initiative that forms part of the Digital Single Market Strategy.
Recent studies continue to show customers want flexible delivery options and one in three consumers prefer to have packages delivered somewhere other than their home. This is not surprising given that 17% of home deliveries fail on first attempt, rising to over 50% in some Member States and 98% of e-retailers think successful delivery is important for repeat purchases. As well as benefitting customers (who get their parcel earlier), by providing fixed time-windows for the delivery or alternative delivery points such as collection points or parcel lockers, the parcel operators also gain as they decrease their delivery costs for the last mile, e.g. by avoiding failed delivery attempts and consolidating delivery locations. Easy and effective 'returns' solutions also benefit e-retailers as they help them to attract and retain customers. Improving returns solutions is especially important in the context of cross-border purchases. In a recent survey of online consumers about obstacles to the Digital Single Market, high delivery costs, high return shipping costs, long delivery times and non-delivery were among the top concerns. Low delivery costs, convenient delivery options (such as time and place of delivery) and the possibility of delivery to the country of the consumer were amount the seven most frequently reported reasons for consumers choosing a certain website. (See section 2.8.2 on the internal market and tariff principles for further information about the price of cross-border delivery services.)
Alongside the Digital Single Market Strategy, the Commission services launched a public consultation on cross-border parcel delivery to seek views from all interested parties on the main issues and possible areas for improvement. The consultation closed in August 2015 and the responses will be used to inform the Impact Assessment for the cross-border parcel initiative.
3.4.Employment in the Postal Sector
3.4.1.Overview
The Postal Services Directive is "without prejudice to the competence of Member States to regulate employment conditions in the postal services sector" although it also notes that the Directive "should not lead to unfair competition" and "social considerations should be taken into account when preparing the opening of the postal market". Sector specific labour regulations do not appear to be used as a barrier to competition, though in some Member States labour requirements form part of the license/authorisation by the regulator.
The labour market in the postal sector has undergone significant restructuring in recent years, primarily driven by the falling number of letters as a result of e-substitution. Technological advances have also brought about modernisation and increasing automation and e-commerce is increasing the number of parcels. In the run up to and following full market opening across the EU from 2013, many national postal services restructured their operations, while in parallel new entrants are expanding their activities and creating jobs. Recent announcements illustrate outsourcing and diversification into parcel networks in response to changes in customer demands and there is also a shift in mix of products that postmen and women deliver as the number of parcels increases while the number of letters falls. As a consequence, the job profiles, tasks and skills needed of postal workers are changing and overall employment, in particular USP employment, has decreased. Many postal operators are also taking steps to create a more flexible workforce better adapted to declining volumes.
Nevertheless, despite these structural changes, postal companies continue to employ large numbers of people. In 2013 about 1.2 million people were employed directly by national postal operators and in some Member States the national postal operators still had a notable proportion of total employment. Other postal operators have also created jobs, though the overall amount cannot be quantified due to a lack of definition of the sector and unreliable data so the net effect of market opening and changes in letter and parcel volumes on employment cannot be quantified with certainty.
The creation of a significant number of jobs following gradual market opening could only have been anticipated if competitors had invested in their own end-to-end delivery networks as delivery is the most labour-intensive activity. Limited comparable information is however available about the size of operators' workforces, other than for universal service providers.
The growth in parcel volumes, together with product and service diversification is also having an impact on employment. One study found that direct employment in the European Express market had grown from 240,000 to 272,000 (full time equivalent) between 2003 and 2010, a rise of over 12%, and predicted that by 2020 the express delivery industry would directly employ 300,000 people.
3.4.2.Employment in Universal Service Providers
Overall employment by universal service providers is declining, driven by declining mail volumes, restructuring and automation.
The figure below shows the number of people employed by the universal service provider in each Member State (where the data is available).
Figure 22: Total Universal Service Provider domestic employment (headcount) 2013
Source: European Commission Postal Statistics Database
Universal Service Providers nevertheless remain large employers and despite workforce reductions, still account for a notable proportion of total employment in some Member States, especially the Czech Republic, Slovakia and Denmark. However the overall net effect on employment of market opening and changes in letter and parcel volumes is difficult to quantify, due to a lack of definition of the sector and unavailability of relevant data, in particular in the parcel and express segment.
Figure 23: Share of Universal Service Providers' domestic employment as percentage of total employment in EU Member States, 2013
Source: European Commission Postal Statistics Database
Figure 24: Average Annual Change in USP Employment 2008-2011
Source: Eurostat
Figure 25: Employment Change in Universal Service Providers between 2012-2013
Source: European Commission Postal Statistics Database
Based on the most recent data available, overall, postal employment decreased on average by 4.4% in the EU28 between 2012 and 2013 and several universal service providers reduced employment by over 8% over the same period. Recent significant reductions have often (though not always) occurred in Member States which liberalised their postal markets later, which have been working to restructure and streamline their universal service providers in order to meet the challenge of increased competition as a result of market opening and technology advances.
Most USPs have a predominantly male workforce. In November 2012 the Commission proposed legislation with the aim of attaining 40% of the under-represented sex in non-executive board-member positions of publicly listed companies, excluding SMEs. Posti, Poste Italiane, Post NL and Correios de Portugal CTT have at least a 40% share of female executives. Lietuvos pastas, Post NL and Royal Mail, are run by female chief executives. In some instances policies are in place to encourage female management talent, for example in Deutsche Post and Post Nord. The CEO of Post NL, Herna Verhagen, has recently been voted the most powerful woman in the Netherlands by the magazine Opzij.
Throughout the European Union, the majority of employees of universal service providers are over 40, however in many Member States, employees over 50 comprise over 50% of the workforce. The International Post Corporation estimate the average age is 44.7 across the industry. In order to raise awareness on the impact of demographic challenges on the postal industry, the EU sectorial social partners have run a joint project funded by the European Commission "Managing demographic challenges and finding sustainable solutions by the social partners in the postal sector" which aims at analysing the impact of demographic changes on the postal industry, share managerial practices regarding age management, both in terms of continued employment for older workers as well as promoting employability and occupational health.
3.4.3.Type of Employment and Working Conditions
Although proportions vary due to outsourcing and diversification of operations, such as financial services, in general a large proportion of universal service providers' employees are involved in delivery operations which is the most labour-intensive activity of the postal value chain. In at least six Member States, this leads to more than half the USPs' staff are active in delivery. However in at least five other Member States, less than 30% of all employees are delivery staff. Delivery operations also make up the bulk of USP's costs, estimated to account for around 60-80% of the total, depending on the Member State. It is now rare for universal service providers to be staffed by civil servants.
In the majority of EU Member States national minimum wage levels exist. There are postal sector specific minimum wages in a small number of Member States. There are two Member States where competitors in the postal sector are neither subject to collective labour agreements nor binding national wage floors. Two universal service providers have workers with contracts not subject to social insurance contributions
Overall there has however been a move towards more flexible employment contracts, for example part-time employment, temporary agency employment or even self-employment. This is linked to the fact that operators are seeking to reduce costs and to respond to falling letter volumes although some employees may prefer more flexible contracts which enable them to balance work with caring responsibilities. Fixed term contracts comprise around 20% of the workforce in a small number of universal service providers and around 10% in nearly a quarter. Some universal service providers make use of agency workers, and in a small number of cases they form over 10% of the workforce. The average share of part-time employees in USPs has largely remained stable at around 20% since 2002. There is however significant variance between Member States, with some USPs having over 40% of their employees on part-time contracts whereas other have a very low proportion of part-time staff.
The extent and the type of flexible employment differs from Member State to Member State, determined largely by demand for such contracts but also by national or sectoral social and labour legislation. While such contracts may be appealing to employees seeking flexibility, 'flexible' contracts may also provide less job security and lower wages than permanent full time employees at the universal service provider. This trend in the postal sector towards non-standard employment contracts is consistent with more general trends towards such flexible forms of employment in the wider economy.
The increasing number of parcels is likely to continue to have an impact on the postal employee’s daily work. Non-standard employment contracts are already commonly used by parcel operators who also use subcontractors and self-employed delivery staff. Working and employment conditions in the courier, parcel and express sector have been criticized in several Member States because of low wage levels and low social security of employees working either as subcontractors or as virtually self-employed delivery staff.
In Germany, many competitors do not use their own delivery personnel but outsource delivery to business partners, in some cases even outsourcing sorting activities. In light of public criticism of working conditions in the German parcel market, some companies have established measures to improve their working conditions. In June 2012, Hermes Europe, a subsidiary of Germany’s biggest distance-seller Otto, introduced a code for “employees and business partners in parcel delivery”. This code stipulates minimum hourly wages of EUR 8.50. Breaches of the code or of legal requirements on working conditions will be prosecuted and may lead to termination of contract with business partners.
In May 2013, DPD, a subsidiary of La Poste’s international parcel provider GeoPost, agreed on a “Corporate Social Responsibility Charter” with unions. The charter defines social minimum standard at GeoPost-companies and serves as a benchmark for business partners.
3.4.4.Social Partners and Industrial Relations
Wages and working conditions at universal service providers tend to be covered by collective labour agreements and working conditions are strongly regulated in all EU Member States. Collective agreements are less common for other postal service providers. Where they do not exist new market entrants agree individually on wages and working conditions with employees, though in some Member States such as Austria and Italy, collective labour agreements of neighbouring sectors apply (e.g. transport or trade sector).
Examples:
In Sweden an agreement governs working conditions for employees of the universal service provider as well as competitors in Sweden and therefore ensures homogenous labour conditions for all market participants. Similar approaches for a sector-wide accord have been initiated in several other Member States.
In the Netherlands, the postal law of 2009 contained an option for the government to be able to issue a decree on working conditions in the postal sector if all of the following circumstances apply: (i) conditions of labour contracts are socially inacceptable (ii) the issue is temporary and limited to the postal sector (iii) the issue cannot be resolved by means of an agreement between employers and representatives of employees. This provision was included in the postal law in order to prevent pressure on labour conditions of the universal service provider in case of full market opening due to self-employed delivery staff at competitive postal operators.
In some Member States collective agreements include provisions to help specifically young workers. La Poste signed an agreement in 2008 seeking to alleviate the difficulties of young workers, especially those from disadvantaged groups, such as those living in areas of high unemployment.
3.4.5.Managing Restructuring
In order to mitigate the effects of the declines in letter volumes, reduce costs and adapt working methods to growing parcel volumes, many postal operators have restructured their operations and invested in new technology. Significant restructuring, including job losses but also job creation, has taken place especially in those Member States which opened their postal markets later.
Posta Romana, Romania’s universal service provider, announced in mid-July 2013 that it intended to cut its workforce of almost 33,000 employees by 3,650. This followed a previous restructuring plan under which the organisation cut around 600 jobs in early 2012 in an effort to reduce costs. Conversely, in April 2013, a private postal services company, Total Post, announced the creation of 180 new jobs as a result of network expansion and market opening.
In Hungary Magyar Posta announced in August 2013 that it had cut 875 jobs in the first quarter of 2013. This was carried out by means of a series of gradual job-reduction measures on the basis of mutual agreement. The company previously opened a centralised logistics centre at Budapest airport in 2011, with the creation of around 270 new jobs.
In some Member States (such as Germany, the Netherlands, and Sweden), which fully opened their postal markets ahead of the 2010 deadline, operators such as Deutsche Post and Post NL
automated many of their processes relatively early and continue to modernise their operations.
Deutsche Post invested c. EUR 400m between 2009 and 2012 to increase automation in its 82 mail centres. Around EUR 750m was also invested in its parcel operations (to 2014), more than doubling capacity.
La Poste launched a EUR 3.4bn modernisation project in 2004 which by 2011 covered 90% of the country. Delivery times improved, though employment was reduced by one fifth. La Poste invested EUR 1.65m in 2013 and EUR 997m in 2014 in its parcels and express services.
Post NL have reduced the number of mail preparation locations from 260 to 145 and announced plans to abolish the area structure and instead centrally manage staff.
Post Nord stated in late 2014 that profitability was unsatisfactory and further cost savings were needed. A programme of cost reductions was planned from Q4 2014 which was expected to reduce the number of employees in administration and support functions by 700-800 and make annual cost savings of SEK 500 million.
In many cases the universal service provider has worked constructively with the trade union to manage change in a socially responsible way. Early retirement, voluntary departure and natural attrition have frequently been used to reduce the number of compulsory redundancies. Measures to improve further education or training have also been introduced to increase the external mobility of employees. In return for refraining from forced layoffs, trade unions have in some cases approved lower starting salaries for newly employed staff and agreed to increases in contracts with more flexible employment conditions.
Bpost, in Belgium, reduced its employees by around 30% between 2005 and 2012 from 35,000 to 25,675 full-time employees. Measures negotiated through collective agreements included options for part time employment, early retirement, performance-based payments, limited hiring of additional staff and a lower wage for new employees.
A far-reaching reorganisation of TNT and PostNL took place on the basis of a social partnership and with a series of collective labour agreements. The mobility programme agreed in 2007 was generally met with approval and viewed as unavoidable by the social partnership, and was accepted as a socially responsible instrument for downsizing. According to information from PostNL the actual number of compulsory redundancies to June 2013 has been less than forty.
Royal Mail agreed a Business Transformation agreement with the Communication Workers Union in 2010 (following from the 2007 Pay and Modernisation Agreement). Half of the 64 mail centres in 2010 are likely to have closed by 2016. Investment continues in parcel capability, with £130m bring invested over five years in handheld technology.
On the European level, structural changes in the postal sector and its social organisation are discussed by the European social dialogue committee represented by PostEurop (employers' organisation) and UNI Europa (workers' organisation). In April 2012, the European Social Dialogue Committee for the Postal Sector (Working Group on Postal Sector Evolution) issued a new ‘joint declaration’ emphasising the significance of social dialogue in the postal sector and its function as a ‘social observatory’ at the European level and in 2013 conducted a project on "Developing a quality postal service in the digital age.
4.Conclusion
Transposition of the Postal Services Directive
All Member States have transposed and implemented the Postal Services Directive as modified by 2008/6/EC. The latter Directive has not been implemented in the European Economic Area.
Regulation of Postal Services
All Member States have independent National Regulatory Authorities, often combining post with the wider communications market. National Regulatory Authorities have a crucial role and in some cases the structural separation between regulatory activities and other aspects of postal policy could be improved. The European Regulators Group for Postal Services (ERGP) has improved coordination, consultation and co-operation between Member States and provided valuable advice to the Commission.
Licenses remain more common than general authorisations and while some Member States have introduced general authorisations, there have also been instances where licenses have been introduced for services which were previously not part of the licensing regime. Some license conditions appear to go beyond what is necessary and justified in the interests of protecting users or achieving another aim of the Directive.
National Regulatory Authorities continue their historic focus on the letters market. More comprehensive regulatory oversight of the parcel market may be needed given the growing number of parcels to develop the full potential of the Digital Single Market and to get a full and accurate picture of developments in the overall postal market.
The Universal Service
All Member States except Germany continue to formally designate the universal service provider, instead of using one of the other mechanisms provided by the Directive. All Member States provide for collection and delivery on at least five working days a week. Some go beyond this, but for letters this is becoming less common. The scope of the universal service obligation in each Member State varies. Some include bulk mail and periodicals, as well as single piece letters and parcels, although again there is a trend towards the reduction of the types of item which fall under the universal service obligation. Some studies on user needs have shown that in general consumers would accept changes to the universal service, but they want improved parcel delivery services.
To help compensate for declining volumes, some universal service providers have significantly increased their basic tariffs in recent years, though in many cases these Member States previously had postal tariffs that were stable or declining in real terms. National Regulatory Authorities use both ex-ante and ex-post approvals to ensure affordability and/or cost-orientation, with single piece domestic tariffs most likely to be subject to ex-ante controls. For single piece domestic items, the tariff principles of affordability, cost-orientation, non-discrimination and transparency tend to be met.
Financing the Universal Service Obligation
Regulatory accounts cover both universal and non-universal services provided by the universal service provider in the majority of Member States. Where detailed regulatory accounts cover only the universal service area, consideration should be given to how this fits with the 'totality principle' identified by the ERGP, i.e. the scope of the regulatory financial reporting should cover the totality of all the activities which contribute to the provision of the universal service, even if some of these activities also contribute also to the provision of products or services outside the USO.
The Annex to this Report contains information for Member States about different approaches to calculate the net costs of the Postal Universal Service Obligation that have been found to be consistent with Annex I of the Postal Services Directive. Clear regulatory accounts and consistent calculations of the net cost and any unfair financial burden are essential given that Member States may opt to use State aid as compensation for any unfair financial burden resulting from the universal service obligation.
Access to Postal Services, Networks and Infrastructure
In 2013 there were around 700,000 post boxes in the EU28 and about 145,000 postal offices (for the universal service provider). Since 2010 number have remained stable or declined, in some Member States by a considerable amount. Other postal operators are also expanding their physical presence, for example through partnership with retail outlets or the creation of parcel collection facilities.
It appears that several Member States have made significant progress towards ensuring more non-discriminatory access to the postal infrastructure. Not all Member States require downstream access, though almost all universal service providers offer special tariffs. Transparent and non-discriminatory access where special tariffs are offered is required in most Member States, though there have been several cases where it has been alleged that the postal operator does not offer access on such terms.
In several Member States national competition authorities have condemned the provider of the universal service for abuse of a dominant position. Cases include the giving of illegal rebates to business customers, margin squeeze and predatory pricing with the consequence of restricting competition. Competition has also been discouraged through some regulatory practices, such as the imposition of far-reaching license conditions for new entrants.
Quality of Service
All universal service providers measure transit time for (domestic and cross-border) letter mail in accordance with CEN standard EN 13850. While transit time targets have remained largely unchanged since 2010, overall domestic transit time performance improved between 2010 until at least 2013 and in most Member States targets are exceeded for priority letters, and in virtually all Member States for non-priority mail. The proportion of intra-EU letter mail exceeding targets did however fall in 2014, although at 90.6% for D+3 in 2014, targets were still being exceeded.
Fewer Member States measure the transit time for parcels and where there are targets, fewer national regulatory authorities have the ability to take corrective action than for letters if targets are not achieved. Intra-EU cross-border parcel delivery performance is not currently measured. With the growing importance of parcel delivery, better performance measurement of parcels as well as the ability of NRAs to tackle parcel delivery performance issues may be developed.
Protection for Users
All Member States have extended user protection obligation to all postal operators, and almost all Member States have appointed a competent national authority to review users’ complaints that have not been satisfactorily resolved by the universal service provider. All Member States ensure that providers of postal services have a transparent, simple and inexpensive procedure for dealing with complaints from users, and most universal service providers have a system of compensation.
Internal Market for Postal Services
Concerns are often raised by consumers and e-retailers about the high cost of cross-border delivery services. List tariffs for individual parcels (within the EU) are estimated to be two to five times higher than domestic prices. Improving cross-border parcel delivery is part of the Commission's Digital Single Market Strategy for Europe and a public consultation was launched in May 2015 to help identify ways the market could be improved.
Data Collection
Although Article 22a has been implemented and information with respect to letters and the universal service area is comprehensive, there is a lack of data regarding the wider postal sector. An understanding of the postal market as a whole is essential to understand market developments and the sustainability of the sector, especially given the growing number of parcels resulting from e-commerce. This is being addresses as part of the Digital Single Market parcel initiative.
Value Added Tax
The VAT exemption for public postal services is implemented in different ways across Member States, compounding the differences in the scope of the USO and creating distortions. However, the postal sector is - among others - subject to the ongoing review of the VAT rules of the public sector.
Competition Cases
There have been a number of findings of anti-competitive behaviour, notably in relation to pricing practices of universal service providers, by National Competition Authorities since 2009. Reasons for this could include opening up of markets to competition, and hence the behaviour of incumbents designed to protect their market share and/or more competitors resulting in an increasing number of challenges of incumbents' behaviour. The Commission did not adopt any antitrust decisions between 2008 and early 2015.
On 7 April 2015 a planned merger of FedEX and TNT was announced, subject to approval by competition authorities.
State aid continues to be used in some Member States, in particular to ensure the provision of postal services in rural areas, low tariffs for certain types of mail (e.g. for electoral candidates) and for restructuring and modernisation. Two decisions found that the undertaking concerned had been overcompensated and some repayment was required. The Annex to this Staff Working Document contains information about approaches to the net cost methodology that have been found to be compatible with Annex I of the Directive.
Letter Post
While parcel and express revenues have grown, demand for letter post services has declined substantially. The number of letter post items dispatched by EU27 universal service providers has fallen from an estimated 107.6 billion in 2008 to 85.5 billion in 2013. Average EU letter mail decline was 4.85% between 2012 and 2013, although some Member States have experienced much steeper annual declines, in some cases over 10% per annum. In general direct mail (advertising) and publications have been less affected than letters.
Demand for postal services in the Member States is heterogeneous and reflects differences in economic development. The Western Member States continue to have the highest letter post and parcel volumes, on average 212 letter post items per capita in 2013, although these are often the countries experience the greatest decline. In contrast, citizens of the Southern and the Eastern Member States received only 72 and 53 letter post items per capita in 2013 on average. In the EU28 the average annual per capita volume for 2013 was 141 letter post items.
Despite full market opening across the EU by 2013, competition in the letters market has been slow to develop in most Member States and only in a few Member States have competitors been able to achieve market shares above 10%. Markets for cross-border letter post are still dominated largely by universal service providers from some Member States.
Parcel Post
Estimates of the size of the European parcel market range from EUR 60 billion in for the combined European courier, parcel and express markets in 2010 to £47 billion (which includes shipments up to 2,500kg) to EUR 37 billion in 2011 to EUR 50 billion in 2015. In contrast to shrinking letter post markets, parcel and express markets are growing substantially. The number of parcels dispatched by universal service providers alone has grown from an estimated 1.65 billion ordinary parcels in 2008 for the EU27 to around 1.96 billion in 2013. Studies coving the full market show growth from EUR 44.7 billion in 2009 to EUR 53.4 billion in 2014. Growth in parcel and express volumes is generally higher than the increase in revenues. This results primarily from a shift from express to deferred parcel services, a higher proportion of B2C shipments, and increasing price competition. Innovation in the market, for example through more convenient delivery and return options, also makes ordering online more appealing.
Domestically, B2C parcel volumes are higher in high income Member States with a tradition of mail ordering and distance selling. Demand is not as strong in many southern and eastern Member States that have lower incomes and lack a tradition of mail order services. However, growth rates in online sales in these markets are high, indicating that e-commerce is also a major driver here. Cross-border e-commerce is much rarer than domestic, and lack of delivery features and high prices for cross-border delivery services are repeatedly amongst the top concerns for both consumers and e-retailers. This is being addressed in the framework of the Digital Single Market Strategy adopted on 6 May 2015, following on from the 2012 Green Paper and the 2013 Roadmap.
Employment
In 2013 around 1.2 million people were employed by universal service providers in the EU and in some Member States universal service providers were responsible for a notable proportion of domestic employment. Other postal operators increase this total, with an estimated 272,000 people directly employed by the express industry in 2010. E-substitution is however leading to reductions in the number of people employed by universal service providers, as are modernisation and growing automation. Between 2008 and 2013 the estimated total number of staff employed by universal service providers fell by around 250,000. Employment by universal services providers decreased at an average rate of 4.4% in the 28 Member States between 2012 and 2013.
Pay levels offered for new entrants has in some Member States decreased and overall there is a trend towards more flexible forms of employment contracts. Operators other than universal service providers appear more likely to use such contracts and they appear to be more prevalent in the parcel sector in which more operators are active. Wages and working conditions at USPs tend to be covered by labour agreements and in many instances trade unions have been important partners as postal operators have modernised their operations. In many instances modernisation has been managed in a socially responsible way alongside the trade union and early retirements and voluntary departures have been used to minimise the number of compulsory redundancies. Despite reductions, a large proportion of staff continue to be involved in delivery operations.
Final Conclusions
Overall the two core aims of European postal policy, namely a minimum range of services of specified quality at affordable prices for all users and market opening with fair conditions of competition, have broadly been achieved, though concerns about the cross-border parcel market persist. Nonetheless, the postal market continues to evolve rapidly and ongoing close monitoring of the overall postal market and the effects of the regulatory framework are needed. This is particularly important in view of the impact, on the universal service obligation, of the decline in letter volumes and the growing number of parcels, and in order to be able to respond, if necessary, to changes in the technical, economic and social environment, and to the needs of users. This is all the more the case given the fundamental need to ensure the sustainability of the sector and its contribution to society. The Commission will publish statistics annually from 2016 to provide regular updates on developments in the letter and parcel markets in the European Union.
5.Annex on the Calculation of the Net Cost of the Postal Universal Service Obligation
Annex I of the Postal Services Directive ( as amended by 2008/6/EC) provides the general methodological framework for calculating the net costs of the Universal Service Obligation (USO). The details of the calculation and the methodological alternatives available are however not dealt with by the Postal Services Directive, but have been studied and applied in practice.
The European Commission, in 2012, commissioned a study to evaluate, among others, how Member States calculate the net costs of the universal service obligation to date. At the same time, the European Regulatory Group for Postal Services (ERGP) had been conducting related research in this field. In addition, there are a number of state aid decisions already adopted by the European Commission related to state aid claims of postal operators who apply Annex I to calculate the net cost of the universal service obligation or of other services of general economic interest (SGEIs).
This Annex presents the different approaches to calculate the net costs of the Postal Universal Service Obligation that have been found to be consistent with Annex I of the Postal Services Directive (2008/6/EC). Those approaches are: the Profitability Cost Approach (PC) and the Net Avoided Cost Approach (NAC). This Annex aims at clarifying how those concepts could be applied in line with Annex I.
Although this Annex presents the general methodologies for calculating the net costs of the USO, the particularities of a given case may justify departing from the methodologies described below. In all cases, any departures from the concepts below need to be clearly and objectively justifiable. In this event, the net cost methodology used should be adapted to meet the particularities of each specific case.
BASIC CONCEPTS AND TERMINOLOGY
Before addressing the key features of the two calculation approaches (PC and NAC) it is useful to present the key concepts of Annex I of the Postal Services Directive (2008/6/EC) and other relevant elements that the calculation should take into account in all cases, irrespectively of the actual methodology applied in practice.
1.The Concept of Counterfactual Scenario
Annex I of the Postal Services Directive introduces the concept of counterfactual market scenario for the calculation of the net costs of the universal service obligation which is incorporated in the "counterfactual methodology". The "counterfactual methodology" is an analytical exercise (put forward by the postal operator and verified by the relevant national regulatory authority) that compares a baseline scenario of a universal service provider designated to provide the universal service obligation with a hypothetical but well justified counterfactual market situation (counterfactual scenario) where the same operator would not be required to provide the obligation, in a liberalised market.
2.Relevant Elements for the calculation of the net cost of the postal Universal Service Obligation
Part B of Annex I of the Postal Services Directive sets out a series of relevant elements that the calculation of the net costs of the universal service obligation takes into account, namely:
(a)intangible and market benefits, which accrue to a designated universal service provider,
(b)the entitlement to a reasonable profit and
(c)incentives for cost efficiency.
(a) Intangible and market benefits
Designated universal service providers may enjoy certain intangible and market benefits over their rivals due to their specific position in the postal market.
In order for an element to be considered a benefit (intangible or market), the following conditions are applied:
(a)The designated universal service provider enjoys an advantage over its rivals;
(b)This benefit has a demonstrable causal link to the universal service obligation.
Intangible and market benefits can include a number of elements, such as:
(c)Brand value effects: (when operators can achieve higher sales due to brand recognition)
(d)Economies of scale and scope: (when operators can achieve lower average costs in providing USO and non-USO products)
(e)VAT exemption: (when operators can achieve higher sales to customers who cannot reclaim VAT)
(f)Ubiquity: (when operators can achieve better customer retention and acquisition when mailers move addresses etc.)
(g)Demand complementarities: (when operators can achieve higher sales on other non-USO products and so on)
(b) Reasonable profits
Incorporating the entitlement to a reasonable profit in the net cost calculation is meant to provide to the universal service provider adequate incentives to invest. The cost of capital concept is used as a reasonable economic measurement of profitability. The Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) is commonly used as a cost of capital concept. It indicates the rate of return which must be generated in order to ensure that investors are willing to maintain their investment under competitive conditions. The WACC associated with the provision of the universal service is appropriate to ensure that all relevant costs of the universal service provider are taken into account. When justified, profit level indicators other than the WACC could instead be used to determine what the reasonable profit should be, such as the Return on Equity (RoE), the Return on Assets (RoA) or the Return on Sales (RoS).
(c) Incentives for Cost Efficiency
The net cost calculation should, as much as possible, reflect costs corresponding to the efficient delivery of the universal postal service. While from a State aid viewpoint, efficiency is not a prerequisite for compensation, when calculating the net costs of the universal service obligation, designated universal service provider(s) should effectively demonstrate that they have included in their calculations sufficient efficiency incentives.
3.Double Counting
Controlling for double-counting is a methodological consideration that has to be taken into account at all steps of the calculation methodology, particularly because failing to control for double counting may result in a serious overestimation of the true benefits or costs of the universal service provision and hence, create distortive effects to the development of competition. This risk is particularly evident when the Universal Service Specification comprises more than one dimension (product and service).
METHODOLOGIES FOR CALCULATING THE NET COSTS OF THE UNIVERSAL SERVICE OBLIGATION
1. Profitability Cost Approach (PC)
Annex I, part B, states that "The net cost of universal service obligations is to be calculated, as the difference between the net cost for a designated universal service provider of operating with the universal service obligations and the same postal service provider operating without the universal service obligations, in a liberalised market".
Several elements are to be taken into account when calculating the PC approach:
I.Counterfactual Scenario under the PC approach
According to the PC approach the counterfactual scenario is “an unconstrained re-specification of the designated universal service provider’s operations and product offer, in a hypothetical situation where the Universal Service Obligation is not imposed to any postal operator, with the aim of maximizing profits as a whole”.
From the above definition, the net costs of the USO are given by the difference between the profit levels of an operator, operating with and without the USO, in a liberalised market, and can be expressed as stated below:
Net Cost of the USO = Π w/uso- Π w-o/uso, where:
Π w/uso=R w/uso -C w/uso
Π w-o-/uso = R w-o/uso -C w-o/uso
When defining the hypothetical situation of a designated universal service provider operating without the universal service obligation a number of hypothetical but well justified situations can be taken into account, for example:
(a)A reduction in the size or ownership of the counters network,
(b)A reduction in frequency of delivery (locally or nationally),
(c)The withdrawal of free mail for the blind, where applicable,
(d)The removal of nationwide or local delivery,
(e)The removal of 1st class mail, where applicable,
(f)The reduction in quality of service targets.
Designated universal service providers should justify that the counterfactual situation they present is feasible and reliable. This could be achieved either for example by systematically assessing the commercial postal market of specific Member States in similar contexts, or by anchoring the counterfactual scenario to the current operational (business) strategy.
II.Cost Concept
The profitability cost approach uses a Long Run Incremental Cost (LRIC) concept to estimate the avoidable costs, absent the Universal Service Obligation. The LRIC of an increment of output is the additional cost that an operator would incur for providing that increment in the long run.
When a LRIC model is deployed, accounting data (cost and financial accounting information) may be supplementary used to calibrate model data, provided that the quality and the granularity of the accounting information allows for that.
III.Demand Effects
The PC approach studies explicitly how demand (non-price demand effects), market shares (non-price market share effects) and prices (price effects) are affected if the Universal Service Obligation will be relaxed.
IV.Intangible and Market Benefits
In accordance with the Profitability Cost Approach intangible and market benefits should only be incorporated in the net cost calculation through an ex-post adjustment to the net result, if and only if, following a reasoned justification, their effect has not already been taken into account in the definition of the counterfactual scenario. The contrary will lead to double counting of their effect.
V.Entitlement to a Reasonable Profit
Allowing for reasonable profits when applying the Profitability Cost approach, transforms the respective net cost formula as follows:
Net Cost of the USO = (Π w/uso -CC w/uso )- (Π w-o-/uso -CC w-o/uso), where:
Π w/uso=R w/uso -C w/uso
Π w-o-/uso = R w-o/uso -C w-o/uso
CC w/uso = Capital Costs w/uso = WACC w/uso * Capital employed w/uso
CC w-o/uso = Capital Costs w-o/uso = WACC w-o/uso *Capital employed w-o/uso
In certain cases, in particular when the capital employed does not vary significantly between the two scenarios, the impact of the difference in capital costs when moving from the baseline to the counterfactual scenario [CC w/uso - CC w-o/uso] might not be considered substantial or material.
VI.Incentives to cost efficiency
As the PC approach uses model cost data in the net cost calculation, efficiency incentives are already embedded in the calculation. In the event that the Profitability Cost Approach uses real cost data for the calculation, as any inefficiencies are already included in both the baseline and the counterfactual scenario, then the impact of the existence of any inefficiencies might be considered to have a second order effect to the result of the calculation.
VII.Double Counting
(1)Controlling for double counting while implementing the Profitability Cost approach is essential, particularly in the events when
a)The USO definition has more than one dimension and involves both product and service specifications.
b)Treating intangible and market benefits.
If the counterfactual scenario is comprised by more than one dimension (i.e. product/service), the calculation of the net cost should follow a sequential approach in order to avoid the double counting of any direct and indirect benefits and costs.
2. Net Avoided Cost Approach (NAC)
Although the Profitability Cost is considered to be the most appropriate method for determining the net costs of a universal service obligation, there may be cases where its use is not feasible or appropriate. That might be the case where there are serious data gaps or market uncertainty that would deem the framing of the counterfactual definition, under the PC approach, rather unrealistic. In such cases, alternative methods may be applied, focusing on the profitability of individual products or services rather than the profitability of the company as a whole.
Part B of Annex I of the Postal Directive sets out that the net cost can be calculated as the sum of the net costs of individual universal service products or services.
The following elements should be taken into account when using the NAC approach:
I.Counterfactual Scenario under the NAC approach
With reference to the net avoided cost methodology, the counterfactual scenario in this case is defined as a situation where the designated universal service provider would cease operations in the unprofitable (loss making) universal services and product categories.
According to the definition above the net cost of the Universal Service Obligation, is given by the sum of the net losses of the loss making mail flows or mailing routes of the USO products/services,, i.e.
Net Cost of the USO = Σi (Ci-Ri), for each Ri-Ci < 0, where:
Ci= total operating costs associated with the USO provision of mail flow i
Ri = revenues associated with the USO provision of mail flow i
The identification of the loss making flows would be subject to certain constraints (see points ii –iii below).
II.Cost Concept under the NAC approach
Applied practice of the NAC approach has shown that the NAC method can use the Fully Allocated Cost (FAC) concept instead of the LRIC. In this event due attention has to be given to the treatment of fixed and common costs associated with the USO products/services. In this case, common costs which have been attributed across services should in principle be excluded unless duly justified, before informing the judgment of which services, mail flows or products are loss making. The discontinuation of the loss making universal services should be justified and accounted at the most appropriate aggregate level.
III.Demand Effects
The revenue to be taken into account in the calculation includes the recorded revenue directly earned from the services attributed to the USO. However, the designated universal service providers should also study the demand effects and the market share effects of the impact of the cessation of delivery of those unprofitable traffic flows on the profitability of other (USO or non-USO) commercial market segments.
IV.Reasonable Profits
Allowing for reasonable profits when applying the NAC approach transforms the respective net cost equation as follows:
Net Cost of the USO = Σi (Ci+ CCi-Ri), for each Ri -Ci- CCi- <0, where:
Ci= operating costs associated with the USO provision of mail flow i
Ri = revenues associated with the USO provision of mail flow i
CCi =cost of capital associated with the provision of USO mail flow i
V.Efficiency incentives
If the costs incorporated in the net cost calculation formula above do not provide adequate incentives for efficiency, an ex post efficiency adjustment should be instead performed, in a level capable to effectively promote incentives to the designated universal service provider(s) to provide universal services cost efficiently.
Efficiency incentives can be designed in different ways to suit best the specificity of each case by performing an ex post efficiency adjustment. This can be based either on a benchmark analysis of an appropriately justified selected range of efficiency indicators, or on historical trends used for forward looking purposes. Efficiency incentives should always take into consideration the quality standards of the Universal Service Obligation on domestic and cross border targets on transit times, as set out in Annex II of the Postal Services Directive and in the relevant national legislation.
VI.Intangible and Market Benefits
With reference to the NAC approach, the consideration of intangible and market benefits, in principle, should net-off the net cost result following an ex-post adjustment to the net cost calculation, unless there are methodological considerations that could justify the contrary.,
Net Cost of the USO = Σi(Ci-Ri)- Σi (Intangible Benefitsi)
UNFAIR FINANCIAL BURDEN
(1)Article 7(3) of the Postal Services Directive suggests that the assessment of the unfairness of the financial burden follows the net cost calculation. In this context, the assessment of whether the calculated net cost of the Universal Service Obligation constitutes an unfair financial burden, is applied to a net cost result that already took into consideration any intangible and market benefits and after the costs have been adjusted to reflect the entitlement for reasonable profit and incentives for cost efficiency.
(2)In C-222/08 European Commission vs. Kingdom of Belgium, 6/10/2012 the Court of Justice defines unfair burden as "… a burden which for each undertaking concerned, is excessive in view of the undertaking's ability to bear it, account being taken for all the undertaking's own characteristics, in particular the quality of its equipment, its economic and financial situation and its market share".
(3)According to ERGP (11) 17, Rev. 1 chapter 5, the mixed set of criteria informing the judgment on the unfairness of the burden could refer to the current market conditions, the financial standing of the enterprise, and the profitability of the service providers as well as other relevant policy considerations as defined by the Member States.
Therefore the concept of unfairness of the burden is mainly linked with the ability of the designated operator to bear it.
The assessment of unfairness of the financial burden should analyse a number of factors that broadly relate to the market position of the enterprise, the market conditions, the degree of competition and the level of profitability in the market.
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION
EUROPEAN COMMISSION











