EUR-Lex Access to European Union law

This document is an excerpt from the EUR-Lex website
Document 32016D0588
Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2016/588 of 14 April 2016 on the approval of the technology used in 12 Volt efficient alternators as an innovative technology for reducing CO2 emissions from passenger cars pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 443/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council (Text with EEA relevance)
Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2016/588 of 14 April 2016 on the approval of the technology used in 12 Volt efficient alternators as an innovative technology for reducing CO2 emissions from passenger cars pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 443/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council (Text with EEA relevance)
Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2016/588 of 14 April 2016 on the approval of the technology used in 12 Volt efficient alternators as an innovative technology for reducing CO2 emissions from passenger cars pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 443/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council (Text with EEA relevance)
C/2016/2129
OJ L 101, 16.4.2016, p. 25–32
(BG, ES, CS, DA, DE, ET, EL, EN, FR, HR, IT, LV, LT, HU, MT, NL, PL, PT, RO, SK, SL, FI, SV)
 No longer in force, Date of end of validity: 31/12/2020; Repealed by 32020D1806
No longer in force, Date of end of validity: 31/12/2020; Repealed by 32020D1806
|
16.4.2016 |
EN |
Official Journal of the European Union |
L 101/25 |
COMMISSION IMPLEMENTING DECISION (EU) 2016/588
of 14 April 2016
on the approval of the technology used in 12 Volt efficient alternators as an innovative technology for reducing CO2 emissions from passenger cars pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 443/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council
(Text with EEA relevance)
THE EUROPEAN COMMISSION,
Having regard to the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union,
Having regard to Regulation (EC) No 443/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 April 2009 setting emissions performance standards for new passenger cars as part of the Community's integrated approach to reduce CO2 emissions from light-duty vehicles (1), and in particular Article 12(4) thereof,
Whereas:
|
(1) |
The application submitted by the supplier Valeo Equipments Electriques Moteur on 3 November 2015 for the approval of the Valeo high efficient alternator with high efficiency diodes, and the application submitted by the supplier Robert Bosch GmbH on 10 June 2015 for the approval of the Bosch efficient alternator with MOS gated diodes (MGD) have been assessed in accordance with Article 12 of Regulation (EC) No 443/2009, Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) No 725/2011 (2) and the Technical Guidelines for the preparation of applications for the approval of innovative technologies pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 443/2009. |
|
(2) |
The information provided in the Valeo and Bosch applications demonstrates that the conditions and the criteria referred to in Article 12 of Regulation (EC) No 443/2009 and in Articles 2 and 4 of Implementing Regulation (EU) No 725/2011 have been met. As a consequence, the Valeo and Bosch efficient alternators should be approved as innovative technologies. |
|
(3) |
By Implementing Decisions 2013/341/EU (3), 2014/465/EU (4), (EU) 2015/158 (5), (EU) 2015/295 (6) and (EU) 2015/2280 (7) the Commission has approved six applications concerning technologies that contribute to improving the efficiency of alternators. Based on the experience gained from the assessment of those applications as well as the Valeo and Bosch applications, it has been satisfactorily and conclusively demonstrated that a 12 Volt (12 V) alternator with a minimum efficiency ranging from 73,4 % to 74,2 %, depending on the powertrain, and a mass not exceeding the mass of the baseline alternator by more than maximum 3 kg meets the eligibility criteria referred to in Article 12 of Regulation (EC) No 443/2009 and Implementing Regulation (EU) No 725/2011 and provides a reduction in CO2 emissions of at least 1 g CO2/km compared to a baseline alternator with an efficiency of 67 %. |
|
(4) |
It is therefore appropriate to provide manufacturers with the possibility to certify the CO2 savings from 12 V efficient alternators that meet those conditions. In order to ensure that only alternators that are compliant with those conditions are proposed for certification, the manufacturer should provide a verification report from an independent verification body confirming the compliance together with the application for certification submitted to the type approval authority. |
|
(5) |
If the type approval authority finds that the 12 V alternator does not satisfy the conditions for certification, the application for certification of the savings should be rejected. |
|
(6) |
It is appropriate to approve the testing methodology for determining the CO2 savings from 12 V efficient alternators. |
|
(7) |
In order to determine the CO2 savings from a 12 V efficient alternator, it is necessary to establish the baseline technology against which the efficiency of the alternator should be assessed. On the basis of the experience gained, it is appropriate to consider a 12 V alternator with 67 % efficiency as a baseline technology. |
|
(8) |
The savings from a 12 V efficient alternator may be partially demonstrated on the test referred to in Annex XII to Commission Regulation (EC) No 692/2008 (8). It is therefore necessary to ensure that this partial coverage is taken into account in the testing methodology for CO2 savings from 12 V efficient alternators. |
|
(9) |
In order to facilitate a wider deployment of 12 V efficient alternators in new vehicles, a manufacturer should also have the possibility to apply for the certification of the CO2 savings from several 12 V efficient alternators by a single certification application. It is however appropriate to ensure that where this possibility is used a mechanism is applied that incentivises the deployment of only those alternators that offer the highest efficiency. |
|
(10) |
For the purposes of determining the general eco-innovation code to be used in the relevant type approval documents in accordance with Annexes I, VIII and IX to Directive 2007/46/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (9), the individual code to be used for the innovative technology for 12 V efficient alternators should be specified, |
HAS ADOPTED THIS DECISION:
Article 1
Approval
The technology used in the Valeo high efficient alternator with high efficiency diodes and in the Bosch efficient alternator with MOS gated diodes is approved as an innovative technology within the meaning of Article 12 of Regulation (EC) No 443/2009.
Article 2
Application for certification of CO2 savings
1. The manufacturer may apply for certification of the CO2 savings from one or several 12 Volt (V) efficient alternators intended for use in M1 vehicles, provided that it complies with the following conditions:
|
(a) |
it is a component used solely to charge the vehicle battery and to power the electrical system of the vehicle when its combustion engine is running; |
|
(b) |
the mass of the efficient alternator does not exceed the mass of the baseline alternator of 7 kg by more than 3 kg; |
|
(c) |
its efficiency is at least:
|
2. An application for the certification of the savings from one or several efficient alternators shall be accompanied by an independent verification report certifying that the alternator or alternators comply with the conditions set out in paragraph 1.
3. The type approval authority shall reject the application for certification if it finds that the alternator or alternators do not comply with the conditions set out in paragraph 1.
Article 3
Certification of CO2 savings
1. The reduction in CO2 emissions from the use of an efficient alternator referred to in Article 2(1) shall be determined using the methodology set out in the Annex.
2. Where a manufacturer applies for the certification of the CO2 savings from more than one efficient alternator referred to in Article 2(1) in relation to one vehicle version, the type approval authority shall determine which of the alternators tested delivers the lowest CO2 savings, and record the lowest value in the relevant type approval documentation. That value shall be indicated in the certificate of conformity in accordance with Article 11(2) of Implementing Regulation (EU) No 725/2011.
Article 4
Eco-innovation code
The eco-innovation code No 17 shall be entered into the type approval documentation where reference is made to this Decision in accordance with Article 11(1) of Implementing Regulation (EU) No 725/2011.
Article 5
Entry into force
This Decision shall enter into force on the twentieth day following that of its publication in the Official Journal of the European Union.
Done at Brussels, 14 April 2016.
For the Commission
The President
Jean-Claude JUNCKER
(2) Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) No 725/2011 of 25 July 2011 establishing a procedure for the approval and certification of innovative technologies for reducing CO2 emissions from passenger cars pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 443/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council (OJ L 194, 26.7.2011, p. 19).
(3) Commission Implementing Decision 2013/341/EU of 27 June 2013 on the approval of the Valeo Efficient Generation Alternator as an innovative technology for reducing CO2 emissions from passenger cars pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 443/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council (OJ L 179, 29.6.2013, p. 98).
(4) Commission Implementing Decision 2014/465/EU of 16 July 2014 on the approval of the DENSO efficient alternator as an innovative technology for reducing CO2 emissions from passenger cars pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 443/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council and amending Commission Implementing Decision 2013/341/EU (OJ L 210, 17.7.2014, p. 17).
(5) Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2015/158 of 30 January 2015 on the approval of two Robert Bosch GmbH high efficient alternators as the innovative technologies for reducing CO2 emissions from passenger cars pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 443/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council (OJ L 26, 31.1.2015, p. 31).
(6) Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2015/295 of 24 February 2015 on the approval of the MELCO GXi efficient alternator as an innovative technology for reducing CO2 emissions from passenger cars pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 443/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council (OJ L 53, 25.2.2015, p. 11).
(7) Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2015/2280 of 7 December 2015 on the approval of the DENSO efficient alternator as an innovative technology for reducing CO2 emissions from passenger cars pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 443/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council (OJ L 322, 8.12.2015, p. 64).
(8) Commission Regulation (EC) No 692/2008 of 18 July 2008 implementing and amending Regulation (EC) No 715/2007 of the European Parliament and of the Council on type-approval of motor vehicles with respect to emissions from light passenger and commercial vehicles (Euro 5 and Euro 6) and on access to vehicle repair and maintenance information (OJ L 199, 28.7.2008, p. 1).
(9) Directive 2007/46/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 5 September 2007 establishing a framework for the approval of motor vehicles and their trailers, and of systems, components and separate technical units intended for such vehicles (Framework Directive) (OJ L 263, 9.10.2007, p. 1).
ANNEX
METHODOLOGY TO DETERMINE THE CO2 SAVINGS OF A 12 V EFFICIENT ALTERNATOR
1. INTRODUCTION
In order to determine the CO2 savings that can be attributed to the use of an efficient alternator in an M1 vehicle, it is necessary to specify the following:
|
(1) |
the testing conditions; |
|
(2) |
the test equipment; |
|
(3) |
the determination of the efficiency of the efficient alternator and the baseline alternator; |
|
(4) |
the calculation of the CO2 savings; |
|
(5) |
the calculation of the statistical error. |
Symbols, parameters and units
Latin symbols
|
|
— |
CO2 savings [g CO2/km] |
|
CO2 |
— |
Carbon dioxide |
|
CF |
— |
Conversion factor (l/100 km) — (g CO2/km) [g CO2/l] as defined in Table 3 |
|
h |
— |
Frequency as defined in Table 1 |
|
I |
— |
Current intensity at which the measurement shall be carried out [A] |
|
m |
— |
Number of measurements of the sample |
|
M |
— |
Torque [Nm] |
|
n |
— |
Rotational frequency [min– 1] as defined in Table 1 |
|
P |
— |
Power [W] |
|
|
— |
Standard deviation of the eco-innovative alternator efficiency [%] |
|
|
— |
Standard deviation of the eco-innovative alternator efficiency mean [%] |
|
|
— |
Standard deviation of the total CO2 savings [g CO2/km] |
|
U |
— |
Test voltage at which the measurement shall be carried out [V] |
|
v |
— |
Mean driving speed of the New European Driving Cycle (NEDC) [km/h] |
|
VPe |
— |
Consumption of effective power [l/kWh] as defined in Table 2 |
|
|
— |
Sensitivity of calculated CO2 savings related to the efficiency of the eco-innovative alternator |
Greek symbols
|
Δ |
— |
Difference |
|
η |
— |
Baseline alternator efficiency [%] |
|
ηEI |
— |
Efficient alternator efficiency [%] |
|
|
— |
Mean of the eco-innovative alternator efficiency at operating point i [%] |
Subscripts
Index (i) refers to operating point
Index (j) refers to measurement of the sample
|
EI |
— |
Eco-innovative |
|
m |
— |
Mechanical |
|
RW |
— |
Real-world conditions |
|
TA |
— |
Type approval conditions |
|
B |
— |
Baseline |
2. TEST CONDITIONS
The testing conditions shall fulfil the requirements specified in ISO 8854:2012 (1).
Test equipment
The test equipment shall be in accordance with the specifications set out in ISO 8854:2012.
3. MEASUREMENTS AND DETERMINATION OF THE EFFICIENCY
The efficiency of the efficient alternator shall be determined in accordance with ISO 8854:2012, with the exception of the elements specified in the present paragraph.
The measurements shall be conducted at different operating points i, as defined in Table 1. The alternator current intensity is defined as half of the rated current for all operating points. For each speed the voltage and the output current of the alternator are to be kept constant, the voltage at 14,3 V.
Table 1
Operating points
|
Operating point i |
Holding time [s] |
Rotational frequency ni [min– 1] |
Frequency hi |
|
1 |
1 200 |
1 800 |
0,25 |
|
2 |
1 200 |
3 000 |
0,40 |
|
3 |
600 |
6 000 |
0,25 |
|
4 |
300 |
10 000 |
0,10 |
The efficiency shall be calculated in accordance with to Formula 1.
Formula 1

All efficiency measurements are to be performed consecutively at least five (5) times. The average of the measurements at each operating point ( ) has to be calculated.
) has to be calculated.
The efficiency of the eco-innovative alternator (ηEI) shall be calculated in accordance with Formula 2.
Formula 2

The efficient alternator leads to saved mechanical power under real-world conditions (ΔPmRW) and type approval conditions (ΔPmTA) as defined in Formula 3.
Formula 3
ΔPm = ΔPmRW – ΔPmTA
Where the saved mechanical power under real-world conditions (ΔPmRW) is calculated in accordance with Formula 4 and the saved mechanical power under type-approval conditions (ΔPmTA) in accordance with Formula 5.
Formula 4

Formula 5

where
|
PRW |
: |
Power requirement under ‘real-world’ conditions [W], which is 750 W |
|
PTA |
: |
Power requirement under type-approval conditions [W], which is 350 W |
|
ηB |
: |
Efficiency of the baseline alternator [%], which is 67 % |
Calculation of the CO2 savings
The CO2 savings of the efficient alternator are to be calculated with the following formula.
Formula 6
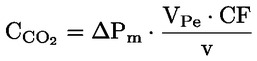
where
|
v |
: |
Mean driving speed of the NEDC [km/h], which is 33,58 km/h |
||||||||
|
VPe |
: |
Is the consumption of effective power specified in the following Table 2 Table 2 Consumption of effective power
|
||||||||
|
CF |
: |
Is the factor specified in the following Table 3 Table 3 Fuel conversion factor
|
Calculation of the statistical error
The statistical errors in the results of the testing methodology caused by the measurements are to be quantified. For each operating point the standard deviation is calculated as defined by the following formula:
Formula 7

The standard deviation of the efficiency value of the efficient alternator ( ) is calculated in accordance with formula 8:
) is calculated in accordance with formula 8:
Formula 8

The standard deviation of the alternator efficiency ( ) leads to an error in the CO2 savings (
) leads to an error in the CO2 savings ( ). That error is calculated in accordance with formula 9:
). That error is calculated in accordance with formula 9:
Formula 9
![]()
Statistical Significance
It has to be demonstrated for each type, variant and version of a vehicle fitted with the efficient alternator that the error in the CO2 savings calculated in accordance with Formula 9 is not greater than the difference between the total CO2 savings and the minimum savings threshold specified in Article 9(1) of Implementing Regulation (EU) No 725/2011 (see Formula 10).
Formula 10

where:
|
MT |
: |
Minimum threshold [g CO2/km], which is 1 g CO2/km |
Test and evaluation Report
The report shall include:
|
— |
Model and mass of the tested alternators |
|
— |
Description of the bench |
|
— |
Test results (measured values) |
|
— |
Calculated results and corresponding formulae |
The efficient alternator to be fitted in vehicles
The type approval authority is to certify the CO2 savings based on measurements of the efficient alternator and the baseline alternator using the test methodology set out in this Annex. Where the CO2 emission savings are below the threshold specified in Article 9(1), the second subparagraph of Article 11(2) of Implementing Regulation (EU) No 725/2011 shall apply.
(1) ISO 8854:2012 Road vehicles — Alternators with regulators — Test methods and general requirements. Reference number ISO 8854:2012, published on 1 June 2012.






